Figure 1.
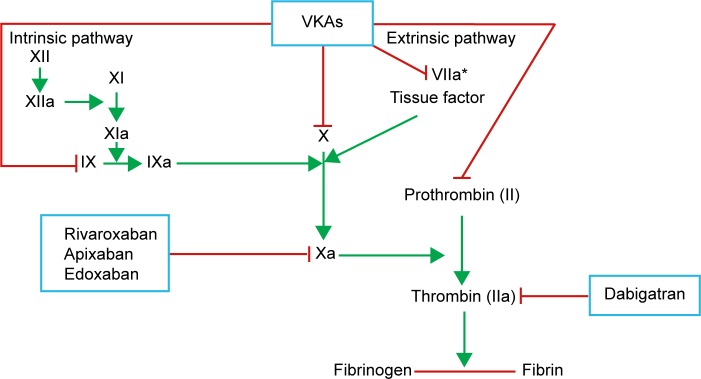
Mechanism of anticoagulants effect of indirect (VKAs) and direct anti-IIa and anti-Xa anticoagulants (NOACs).
Note: *VKA does not inhibit FVIIa, but prevents their synthesis, like other vitamin K-dependent factors (eg, II, IX, and X).
Abbreviations: NOACs, non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants; VKAs, vitamin K antagonists; FVIIa, activated factor VII.
