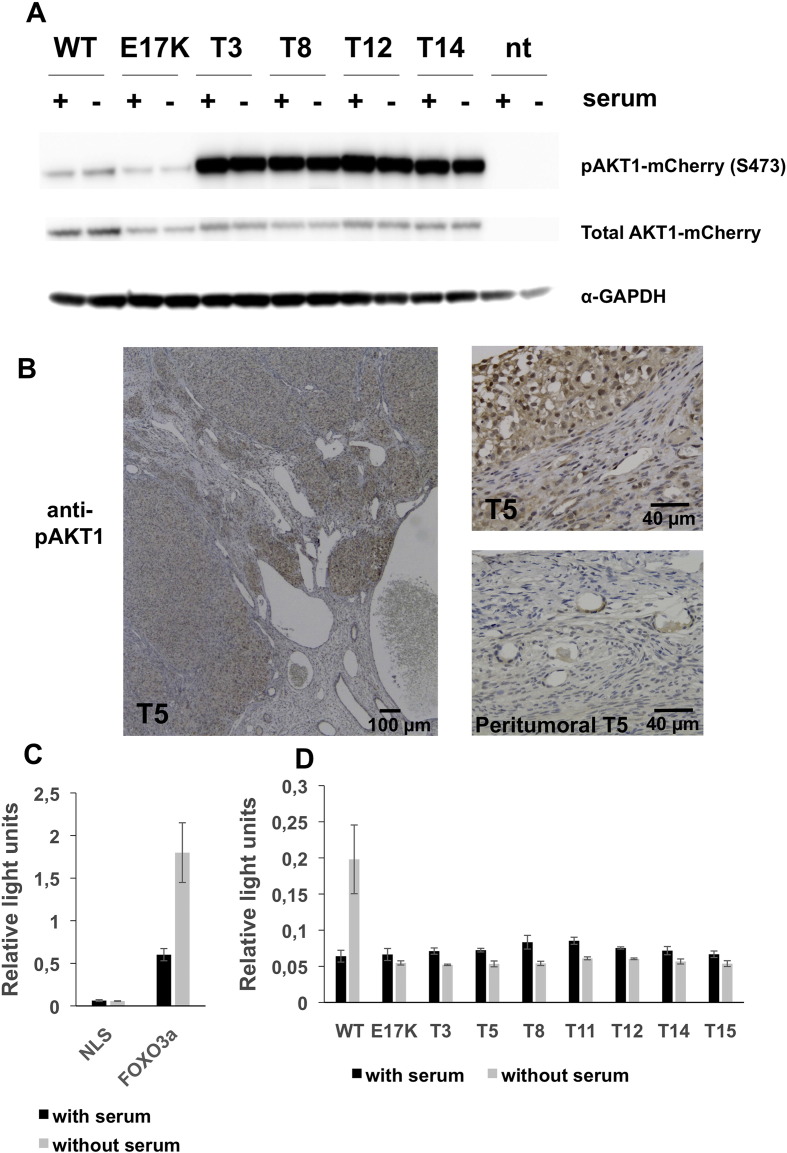
Fig. 6.
Mutated AKT1 phosphorylation and activation levels.
A) Western-blot analysis of the phosphorylation levels of several AKT1 variants (wild-type/WT, E17K and 4 elongated proteins). nt: not transfected. Note that for similar amounts of total AKT1-mCherry, the mutated proteins carrying the duplications are intensely phosphorylated compared to the wild-type protein and to the E17K variant, which is our control of activating mutation. The anti-GAPDH shows that similar protein amounts were loaded in each lane, showing that cell cultures were treated and transfected very similarly. B) Anti-phospho-AKT immunostaining of a section of a tumor (T5) harboring an AKT1 tandem duplication. A section of the nearby, apparently healthy, ovarian tissue also stained with the anti-pAKT is displayed for comparison. C) Effect of the FOXO3a on the 4X-DBE-luc reporter (NLS stands for a control vector) in transfected HeLa cells in the absence or presence of serum. D) Effect of AKT1 variants on FOXO3a transactivation (note that the scale is different with respect to 6C). Here, the cells were co-transfected with 4X-DBE-luc and the various constructs driving the expression of wild-type or mutated AKT1 forms. AKT1-dependent phosphorylation of FOXO3a causes its cytoplasmic sequestration and prevents transactivation of its targets. In the presence of serum, FOXO3a was repressed by phosphorylated wild-type AKT1. In serum-starved cells, wild-type AKT1 repressed FOXO3a far less strongly. The AKT1 proteins bearing the duplications are hyperactive like the E17K mutant. In our experimental setting, this luciferase assay behaved in a rather binary way. This may explain why the impact of E17K and the duplications on AKT1 activity (measured via FOXO3a transactivation) are similar, despite the striking differences of their phosphorylation levels. Error bars represent the standard deviation of 3 replicates. The results are representative of two independent experiments. The differences between the wild-type and mutated AKT1 (in the absence of serum) estimated by a two-sided Student's t-test were all highly significant (p < 0.01).