Fig. 1.
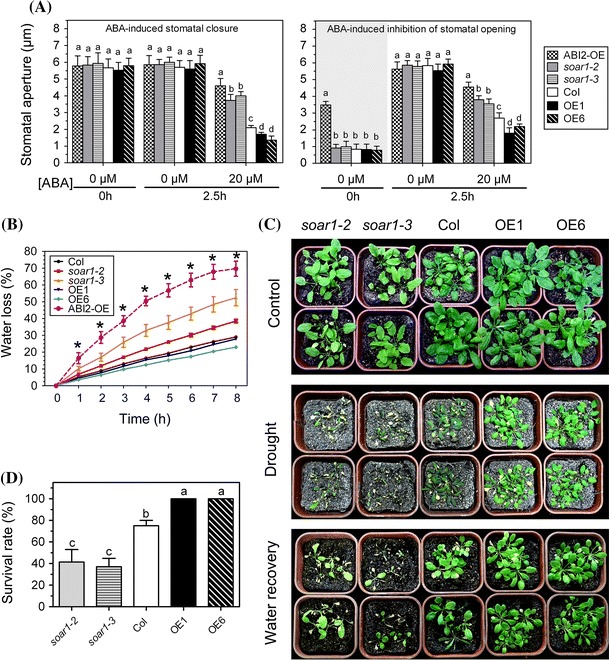
SOAR1 positively regulates plant resistance to drought stress. a ABA-induced stomatal closure (left panel) and inhibition of stomatal opening (right panel) of the wild-type Col, two SOAR1-knockdown mutant alleles soar1-2 and soar1-3, SOAR1-overexpressing lines OE1 and OE6, and an ABI2-overexpressing line ABI2-OE. Mature rosette leaves from 4-week-old seedlings were used for the assays. Values are the mean ± SE from three independent experiments (n ≥ 80 apertures per experiment), and different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 (Duncan’s multiple range test) when comparing values within the same ABA concentration. b Water loss rates during a 6-h period from the detached leaves of the different genotypes described in (a). Values are the mean ± SE of five independent experiments. Star indicates that significant differences at P < 0.05 (Duncan’s multiple range test) exist when comparing values within the same time point. The entire experiment was replicated five times with similar results. c Plant growth status in the drought assays. Drought was imposed on the wild-type Col, soar1-2 and soar1-3 mutants, as well as OE1 and OE6, by withholding water for about 3 weeks until the lethal effect was observed on the mutant plants, while the control plants were well watered. The growth status was recorded 3 days after the plants were re-watered. The entire experiment was replicated three times with similar results. d Survival rate of different genotypes as mentioned in (c). Drought was imposed on the plants by withholding water until the lethal effect was observed on the mutant plants, then survival rate was recorded 3 days after the plants were re-watered. Values are the mean ± SE from three independent experiments (n ≥ 50 plants per line for each experiment) and different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 (Duncan’s multiple range test)
