Figure 2.
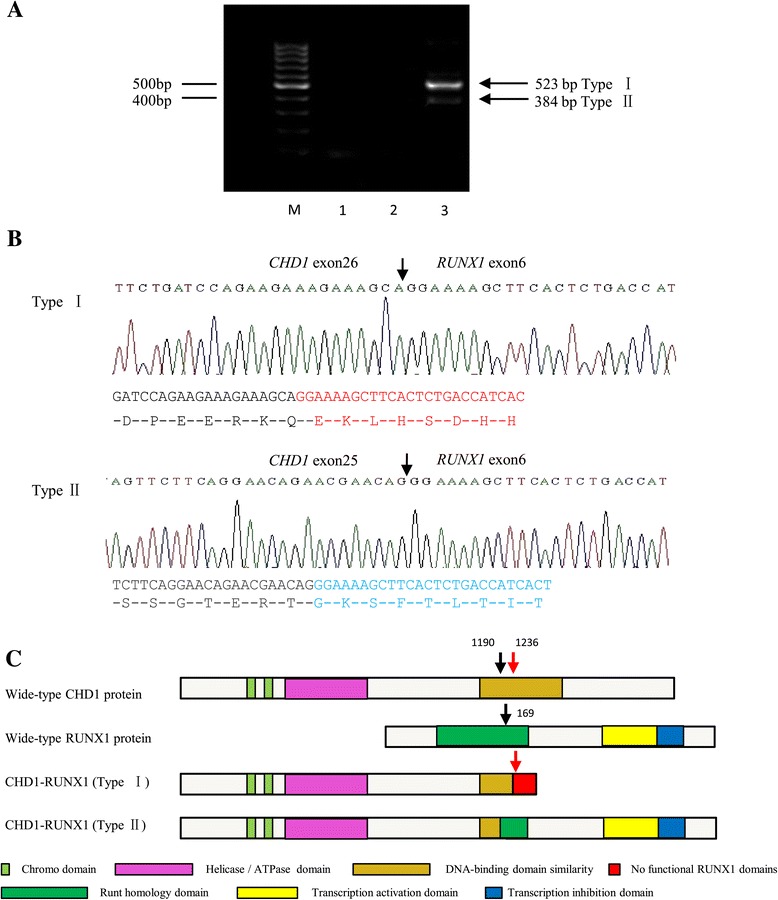
Characterization of the CHD1-RUNX1 fusion. A) RT-PCR confirmation for the CHD1-RUNX1 fusion. Lane M: 100 bp ladder; Lane 1: reagent control; Lane 2: negative control from a normal individual; Lane 3: CHD1-RUNX1 transcripts (523 bp and 384 bp) were detected in the patient discussed here. B) Sequencing analysis revealed two variant fusion transcripts between CHD1 and RUNX1.TypeI was a fusion between exon 26 of CHD1 and exon 6 of RUNX1, Type II was a fusion between exon 25 of CHD1 and exon 6 of RUNX1.The arrows indicated the fusion junction between CHD1 and RUNX1, the arabic numbers (1190, 1236, 169) indicated the amino acids position. C) Schematic structures of chimeric fusion proteins. The TypeII fusion protein retained the RUNX1 inhibition domain, however, the TypeI fusion created a frameshift and stop codon in the RUNX1 region, which resulted in a truncated protein without functional RUNX1 domain.
