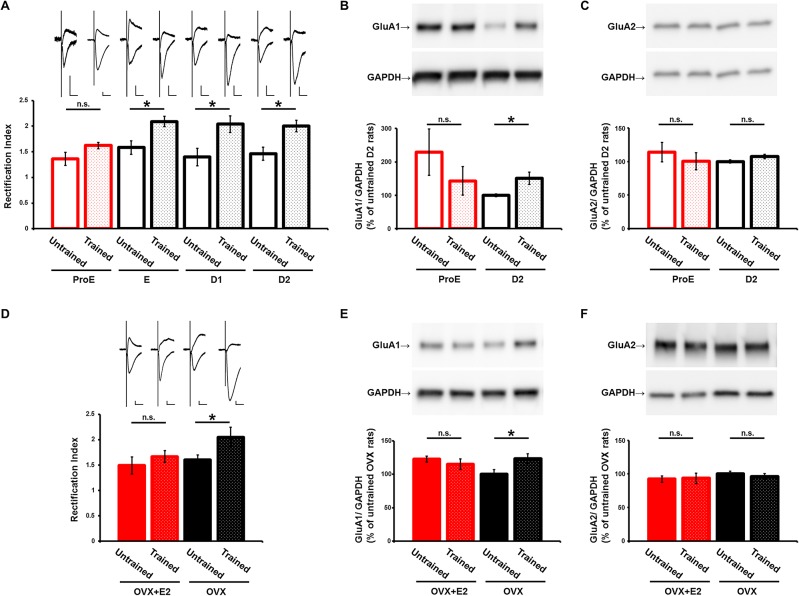
Fig 2. Changes in learning-driven synaptic delivery of CP-AMPARs in CA1 pyramidal neurons during the estrous cycle.
(A) There was no difference in rectification in between untrained (n = 13) and IA-trained (n = 32) ProE rats. However, rectification increased notably after IA conditioning during other periods of the estrous cycle (untrained/ IA-trained: E, n = 11/ 32; D1, n = 7/ 16; D2, n = 9/ 28). (D) Rectification increased after IA conditioning in OVX rats that were not primed with E2 (untrained, n = 19; IA-trained, n = 16), but rectification did not change after IA conditioning in the presence of E2 (untrained, n = 13; IA-trained, n = 11). Scale bars: vertical, 20 pA; horizontal, 20 ms. (B, E) GluA1 and (C, F) GluA2 content in the synaptoneurosome fraction obtained from the rat dorsal hippocampus in ProE (untrained, n = 6; IA-trained, n = 6), D2 (untrained, n = 11; IA-trained, n = 16), and OVX rats with (untrained, n = 7; IA-trained, n = 7) or without E2 priming (untrained, n = 7; IA-trained, n = 7). *P < 0.05; Mann-Whitney U test (A, D) or unpaired Student’s t test (B-F). Error bars represent SEM.