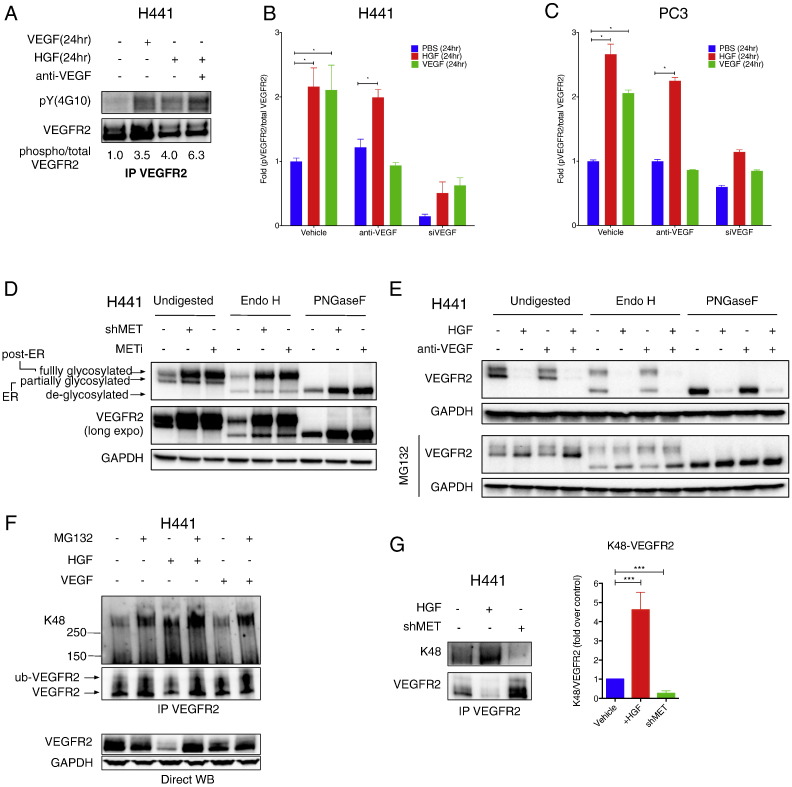
Fig. 4.
HGF induces post-translational modification of VEGFR2.
(A) Effect of exogenous VEGF or HGF on VEGFR2 phosphorylation. H441 cells were cultured with Na3VO4 (100 μM) and treated with HGF or VEGF (100 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of anti-VEGF antibody (10 μg/ml). Cell lysates were then subjected to VEGFR2 IP and analyzed by immunoblot phospho-VEGFR2 (top) or total VEGFR2 (bottom).
(B) H441 cells were treated as in A and phospho-VEGFR2 or total VEGFR2 levels were measured by ELISA. VEGF knockdown (siVEGF) was tested for comparison. Error bars indicate S.E.M., n = 3; *p < 0.05 for indicated comparison.
(C) Same as (B) for PC3 cells.
(D) Effect of Endo H or PNGaseF digestion on migration of VEGFR2. H441 cells were treated with or without shMET or METi (GDC-0712, 1 μM) for 24 h. Cell lysates were then incubated with buffer (undigested), Endo H, or PNGaseF and VEGFR2 and MET were analyzed by IB.
(E) (Left panel) Effect of proteasome inhibitors on HGF modulation of VEGFR2. H441 cells were treated with HGF (100 ng/ml) with or without anti-VEGF (10 μg/ml) for 24 h in absence or presence of MG132 (10 μM) and VEGFR2 levels were analyzed by IB. (Middle and right panels) same samples as shown in left panel but treated with either Endo H or PNGaseF.
(F) Effect of HGF or VEGF on K48-linked ubiquitination of VEGFR2. H441 cells were treated with 100 ng/ml HGF or VEGF in the absence or presence of MG132 (10 μM). Cell lysates were subjected to VEGFR2 IP under denaturing conditions and immunoblotted with K48-ubiquitin antibody (top) or analyzed by direct VEGFR2 immunoblot (bottom).
(G) H441 cells were treated with HGF (100 ng/ml) or subjected to MET knockdown (shMET) and K48-ubiquitinated or total VEGFR2 was detected as in E. Densitometric analysis of several experiments is shown on the right. Error bars indicate S.E.M., n = 5; ***p < 0.005 for indicated comparison.