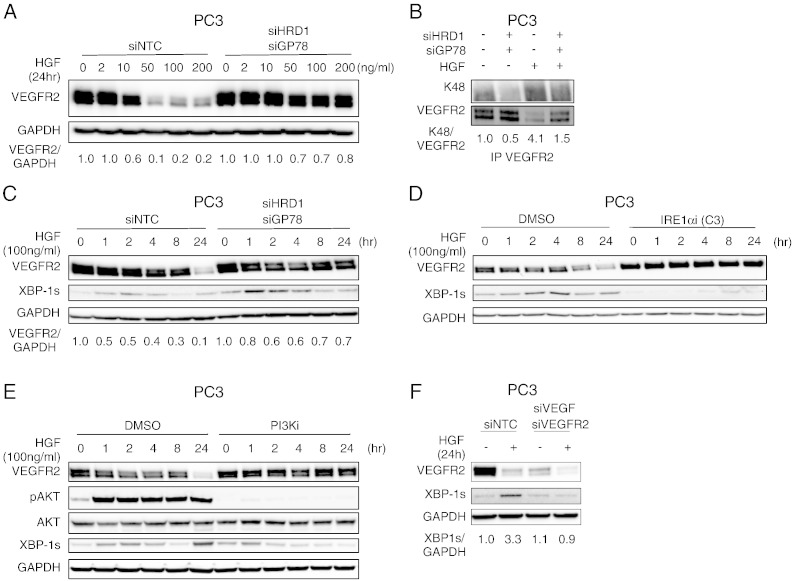
Fig. 5.
HGF induces VEGFR2 depletion via IRE1α/XBP-1s and ERAD.
(A) Effect of HRD1 and gp78 knockdown on HGF modulation of VEGFR2. PC3 cells were transfected with control siRNA or siRNAs targeting HRD1 and gp78 for 48 h, treated with HGF at the indicated concentration for 24 h, and analyzed by immunoblot.
(B) PC3 cells were subjected to siRNA knockdown as in A, treated with vehicle or HGF (100 ng/ml) for 24 h, and K48-linked VEGFR2 was analyzed by immunoblot.
(C) PC3 cells were treated as in (B) for the indicated time. Total VEGFR2 and spliced XBP-1 (XBP-1s) levels were then analyzed by immunoblot. Densitometric analysis of VEGFR2 normalized to GAPDH is shown below.
(D) PC3 cells were treated with HGF for the indicated time in the presence of either vehicle (DMSO) or 10 μM IRE1α kinase inhibitors (Compound 3); VEGFR2 and XBP-1s levels were analyzed by immunoblot.
(E) Cells were treated as in (D) in presence of vehicle or 10 μM PI3K inhibitor (GDC-0941). VEGFR2, phospho-AKT/total AKT, and XBP-1s were then analyzed by immunoblot.
(F) PC3 cells were transfected with scrambled siRNA (siNTC), or siRNA against VEGF (siVEGF) and VEGFR2 (siVEGFR2) for 48 h. Cells were then treated with vehicle or HGF (100 ng/ml). VEGFR2 and XBP-1s levels were then analyzed by immunoblot. Densitometric analysis of XBP-1s normalized to GAPDH is shown below.