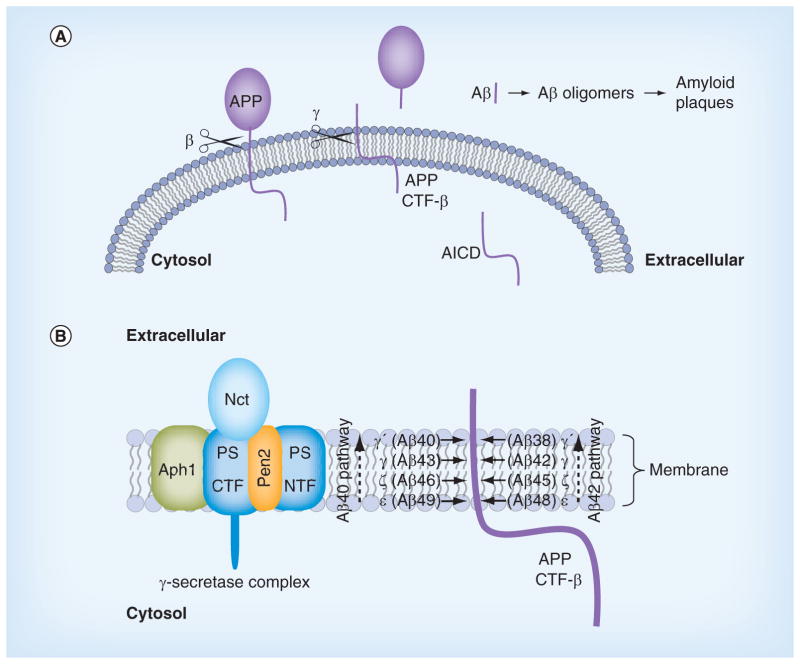
Figure 1. Production of amyloid β-peptide from amyloid precursor protein.
(A) APP is an integral membrane protein, with the Aβ portion derived in part from the single transmembrane domain. β-secretase (β scissors) cleaves outside the membrane to release the large extracellular domain of APP. The membrane-bound remnant is then cleaved within the transmembrane domain by γ-secretase (γ-scissors) to produce Aβ and the AICD. The aggregation-prone Aβ peptide forms neurotoxic oligomers and amyloid plaques. (B)γ-secretase is composed of four different membrane proteins, with the presenilin N-terminal and C-terminal fragment heterodimer as the catalytic component that carries out proteolysis within the APP transmembrane domain. The protease complex initially cuts at the ε sites to produce long Aβ peptides Aβ48 or Aβ49. The enzyme then trims these long Aβ peptides in increments of 3–4 amino acids (at the ζ, γ and γ′ sites) along the Aβ40 or Aβ42 pathways.
Aβ: Amyloid β-peptide; AICD: Amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain; APP: Amyloid precursor protein.