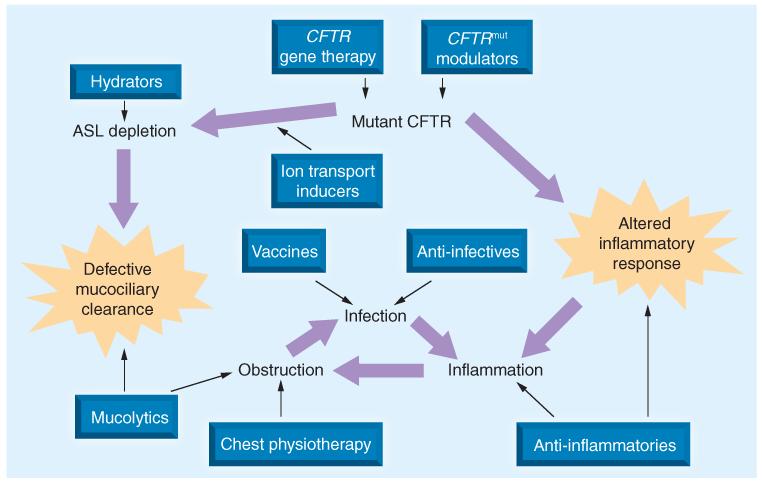
Figure 3. Cystic fibrosis lung disease therapeutic targets.
Physiological ramifications of reduced CFTR activity in the cystic fibrosis lung are highlighted by large arrows. Therapeutic classes that have been and/or are being investigated for the chronic management of cystic fibrosis lung disease are shown in boxes, including CFTR gene therapy [127,128], small-molecule CFTR modulators [34,35,81-84], ion channel recruiters [36], hydrators [30,53], mucolytics [25], anti-infectives [27,31-33,52], vaccines [129] and anti-inflammatories [26,47,50]. Despite different mechanisms of action, all share the goal of reducing lung disease damage caused by the interplay of obstruction, infection and inflammation.