FIGURE 5. Model showing how CF may regulate glucose-6-phosphatase, glucose, and group size.
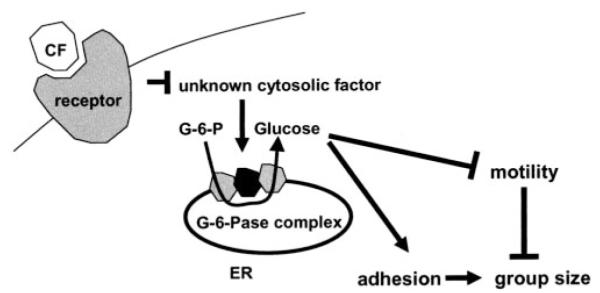
Our working hypothesis is that when CF binds to its surface receptor, this signal inhibits an unknown cytosolic protein. In the absence of CF this protein increases glucose-6-phosphatase activity by decreasing the Km to produce more glucose. A protein found in wild-type cytosol that affects glucose-6-phosphatase may be the same cytosolic protein or may be a different protein. Glucose inhibits cell motility and increases cell-cell adhesion to increase group size. ER, endoplasmic reticulum.
