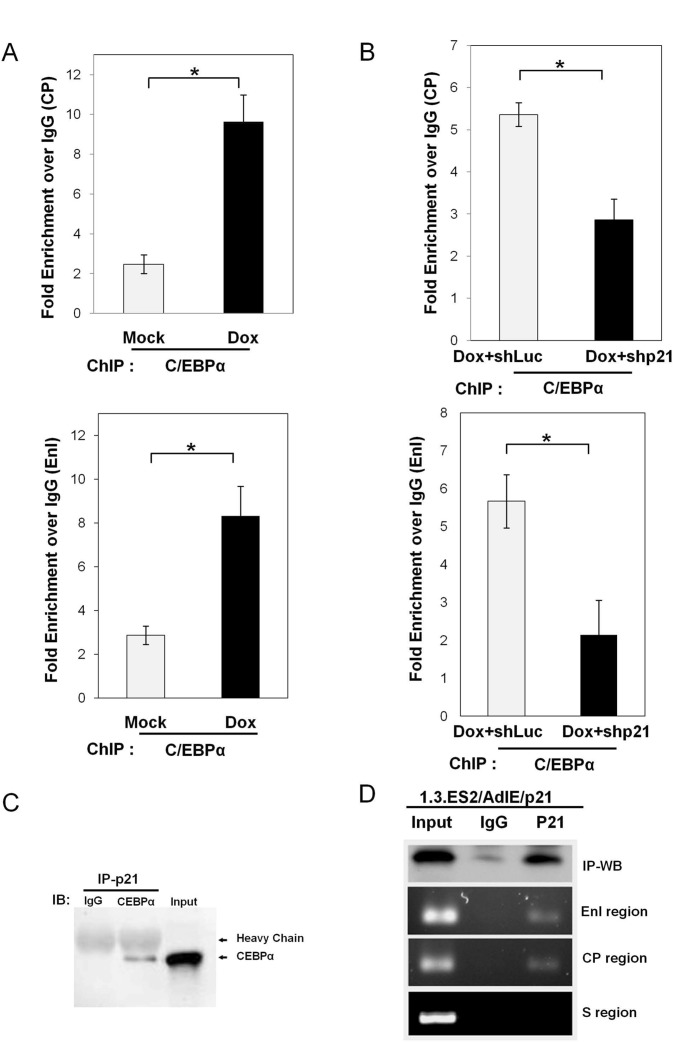
Fig 5. Binding of C/EBPα to the HBV promoter(s) is modulated by doxorubicin and p21.
(A) Doxorubicin enhances C/EBPα recruitment to CP and EnI. 1.3.ES2 cells and doxorubicin-treated 1.3.ES2 cells were harvested in order to carry out ChIP assays. The nuclear extracts were co-incubated with IgG or anti-C/EBPα antibody and the content of the enriched chromatin fragments obtained were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. (B) P21 modulates C/EBPα recruitment to CP and EnI in doxorubicin-treated 1.3.ES2 cells. 1.3.ES2 cells were infected with lentivirus expressing p21 shRNA or control shRNA (shLuc) and this was followed by doxorubicin treatment. The nuclear extracts were harvested for ChIP analysis of the binding efficiency of C/EBPα to CP and EnI. The enrichments of chromatin fragments were determined by quantitative RT-PCR. (C) The protein-protein interaction between p21 and C/EBPα. HepG2 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing C/EBPα and p21 and then the cell lysates were precipitated with anti-p21 antibody, followed by immunoblotting with IgG or anti-CEBPα antibody. The co-immunoprecipitation assay shows the interaction between C/EBPα and p21. (D) A ChIP assay was used to determine the in vivo binding of p21 onto the HBV promoter region in 1.3.ES2 cells. The 1.3.ES2 cells were transduced with AdIE/p21 for 3 days and then collected for the ChIP assay using IgG and p21 antibody. Three pairs of PCR primers for the detection of the EnI region, CP region and S region were designed and used to amplify the immunoprecipitated HBV DNA fragments. *, p < 0.01, 2-sided unpaired t test.