Figure 2.
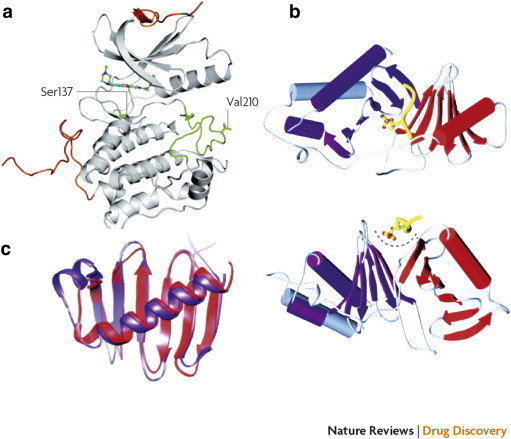
Crystal structure of the N-terminal kinase domain (a) and C-terminal PBD (b) and (c) of human Plk1. (a) The crystal structure of the kinase domain was determined in complex with the pyrrolo-pyrazole inhibitor PHA 680626 at 2.4-Å resolution. The N-terminal and C-terminal extensions are shown in orange, and the activation loop is shown in green. The regulatory phosphorylation site Thr210 was mutated to Val210 to reduce conformational heterogeneity. The position of Ser137, which has been proposed as an additional phosphorylation site for the activation of the kinase activity of Plk1, is also indicated. (b) The crystal structure of the PBD is shown as a ribbon diagram from two different angles in complex with a phosphothreonine-containing peptide (shown in yellow). Polo-box 1 and polo-box 2 are shown in red and purple, respectively. The polo-cap at the N-terminal end of polo-box 1 (gray) folds around polo-box 2, tethering it to polo-box 1 and forming a pocket to accommodate the phosphopeptide. (c) A superposition of the polo-box 1 and polo-box 2 structures is shown (colors indicated in b). Each polo-box consists of a six-stranded β-sheet and an α-helix, which associate to form a 12-stranded β-sandwich domain. This structure documents an interaction along a positively charged cleft formed between the two polo-boxes. Reprinted with permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd, copyright (2010) [3].
