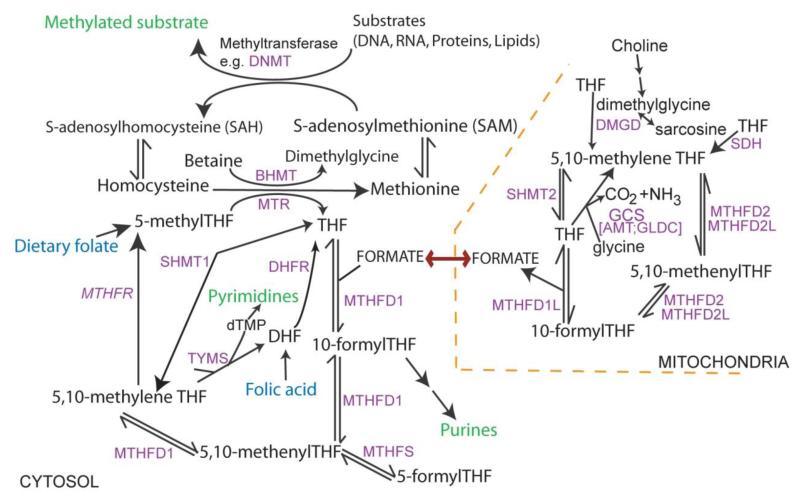
Figure 2. Overview of folate one-carbon metabolism.
Folates provide a backbone for the transfer of one-carbon units. Key outputs (in green) include nucleotide biosynthesis and methylation. Among methylation cycle intermediates, homocysteine may also be converted to cystathionine in the transulfuration pathway and S-adenosylmethionine is involved in polyamine biosynthesis. FOCM is compartmentalised: one-carbon units from the mitochondria enter cytoplasmic FOCM as formate while reactions of thymidylate biosynthesis also operate in the nucleus (catalysed by SHMT1, TYMS and DHFR). In loss-of-function mouse models, NTDs arise in mutants for Mthfd1l and genes encoding the glycine cleavage system (GCS). Shmt1 and Mthfr null mice are viable to birth but may develop NTDs under folate-deficient conditions.