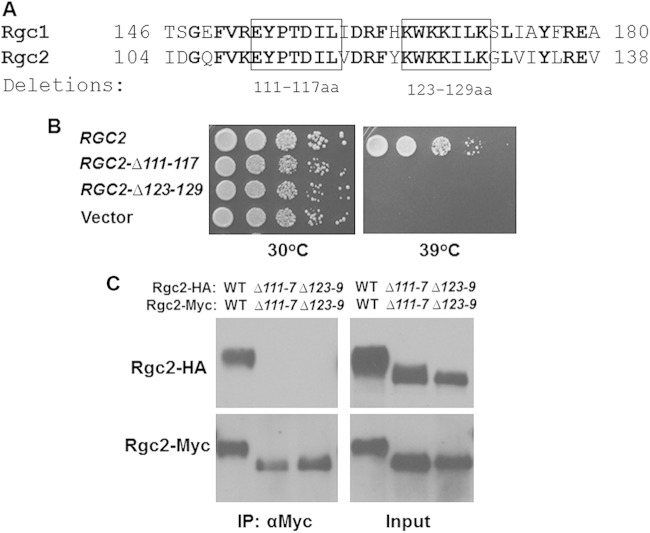
FIG 5.
A region within the N-terminal domain of Rgc2 is essential for self-association and function. (A) Sequence alignment of highly conserved region within the N-terminal domains of Rgc1 and Rgc2. Boxes indicate the short regions targeted for deletion. (B) N-terminal deletion mutants of RGC2 were tested for the ability to complement the temperature sensitive cell lysis defect of an rgc1Δ rgc2Δ mutant as in Fig. 4. (C) Extracts from rgc1Δ rgc2Δ cells (DL3207) cotransformed with plasmids expressing the indicated form of Rgc2-HA or Rgc2-Myc were tested for co-IP by immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblot analysis.