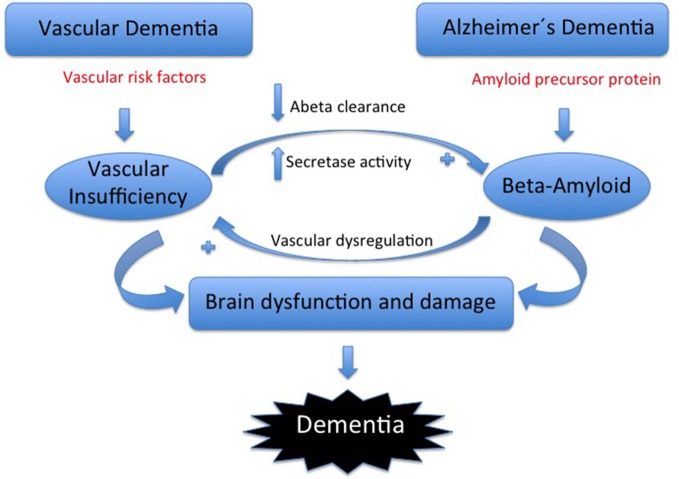
Figure 1.
In VaD, cerebrovascular risk factors induce neurovascular dysfunction leading to brain dysfunction and damage. In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), cleavage of amyloid precursor protein by by β- and γ-secretases leads to Aβ accumulation, which also causes brain dysfunction and damage. Although individually these pathways are capable of inducing cognitive impairment, their interaction enhances their pathogenic effects. Thus, Aβ induces vascular dysregulation and aggravates vascular insufficiency, thereby enhancing the brain dysfunction and damage associated with vascular risk factors. In addition, the hypoxia-ischemia resulting from the vascular insufficiency increases Aβ cleavage from APP and reduces Aβ clearance through the cerebral vasculature, promoting Aβ accumulation and the attendant deleterious effects on the brain (Iadecola, 2010).