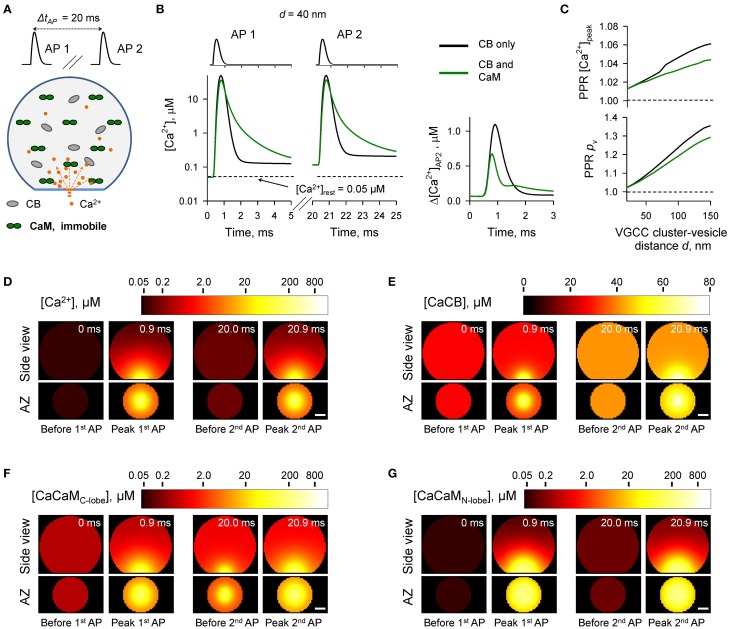
Figure 4.
Effect of immobile CaM on short-term synaptic plasticity. (A) Schematic representation of the paired-pulse simulation experiment (ΔtAP = 20 ms) with immobile CaM, see text for details. (B) Comparison of [Ca2+] time courses at the vesicular release Ca2+ sensor for a representative coupling distance d = 40 nm during paired-pulse stimulation (AP 1 and AP 2) with and without immobile CaM in the presynaptic bouton. Left, [Ca2+] transients; right, net increase of [Ca2+] at the second AP. (C) Dependencies of PPR[Ca2+]peak and PPRpv on the coupling distance d. (D–G) Snapshots of spatial distribution of Ca2+ (D), Ca2+ bound to CB (E), and Ca2+ bound to the C-lobe (F) and the N-lobe (G) of CaM during paired-pulse stimulation. Side view, XZ plane through the center of the bouton (as in A); AZ, 10 nm thick plane immediately above the AZ. Scale bar 100 nm.