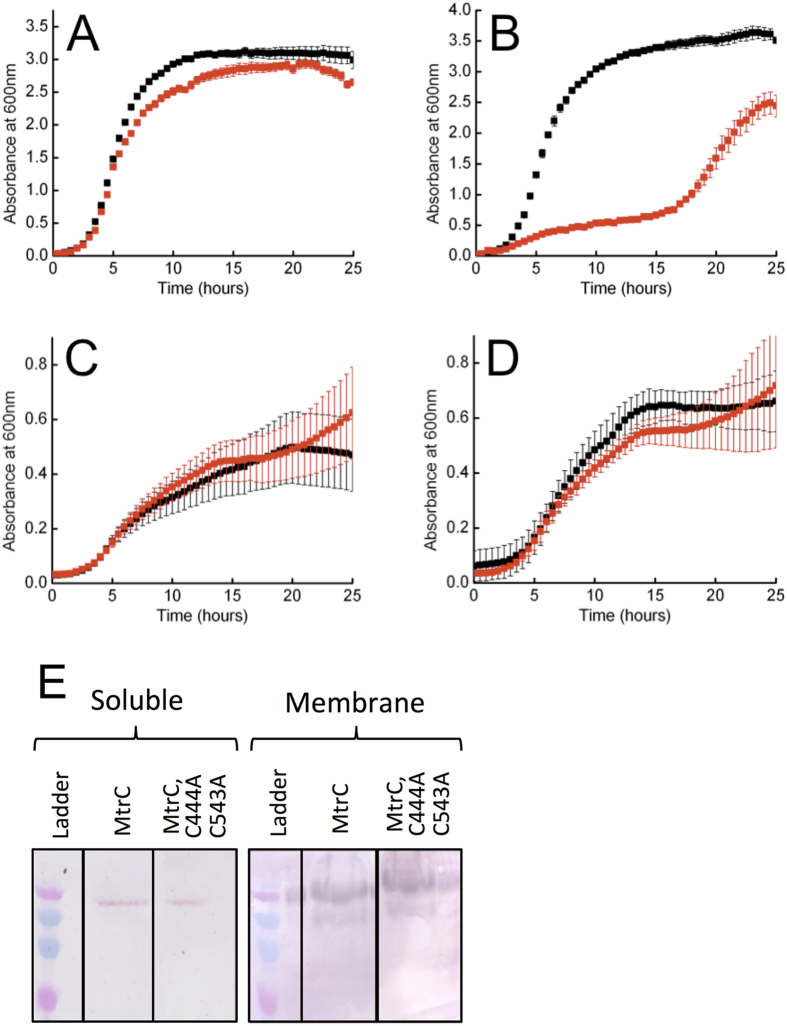
Figure 2. Growth rates and MtrC expression by Shewanella oneidensis LS661 complemented with plasmid pLS172 or pLS172-C444A,C453A.
(A) S. oneidensis LS661 transformed with pLS172 and grown aerobically in the presence of 1 μM FMN and either 0 mM arabinose (black squares) or 10 mM arabinose (red squares). (B) S. oneidensis LS661 transformed wih pLS172-C444A,C453A and grown aerobically in the presence of 1 μM FMN and either 0 mM arabinose (black squares) or 10 mM arabinose (red squares). (C) S. oneidensis LS661 transformed with pLS172 and grown anaerobically in the presence of 1 μM FMN and either 0 mM Arabinose (black squares) or 10 mM arabinose (red squares). (D) S. oneidensis LS661 transformed with pLS172-C444A,C453A and grown anaerobically in the presence of 1 μM FMN and either 0 mM arabinose (black squares) or 10 mM arabinose (red squares). The error bars show the standard deviation for 3 repeats of each experiment. (E) Western blot analyses of soluble and membrane solubilized fractions of Shewanella oneidensis LS661 expressing recombinant MtrC or MtrCC444A,C453A. Cells were induced with arabinose and separated into soluble and membrane fractions. Membrane fractions were subsequently solubilized using Triton X100. The presence of MtrC was detected using antibodies specific to the MtrC sequence position 399-410 and visualised using an alkaline phosphatase conjugated secondary antibody.