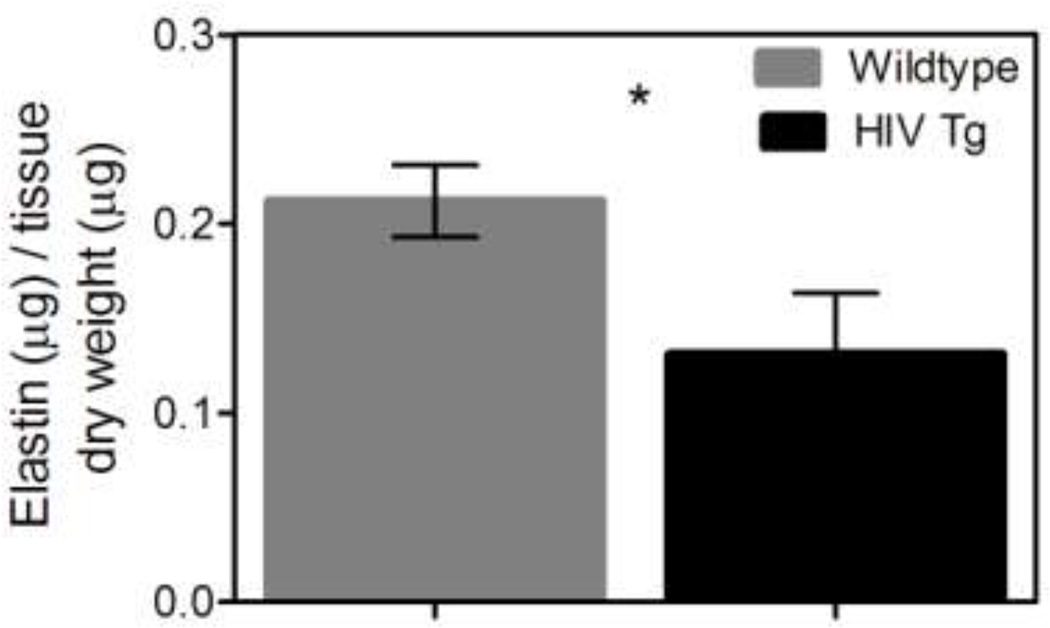
Figure 6. HIV-1 protein expression decreases elastin content.
The normalized elastin content of the suprarenal aortas and carotids was determined using the Fastin assay (Biocolor). The HIV Tg aorta had significantly less elastin than the wildtype as shown (HIV Tg = 0.13 µg elastin/µg dry tissue and wildtype= 0.21 µg elastin/µg dry tissue) (* indicate p<0.05, N=6, and data is mean +/− SEM). The elastin content of the carotids was not significantly different but had values of 0.32 and 0.37 µg elastin/µg dry tissue for HIV Tg and wildtype respectively (p=0.21 N=9). This decrease in elastin aligns with our findings of increased stiffness in the HIV Tg arteries. Collagen content was also assessed using Sirus red staining. The HIV Tg mice had a non-significant trend of more collagen for both the aorta and carotids (p=0.069 N=6 and p=0.18 N=5 respectively).