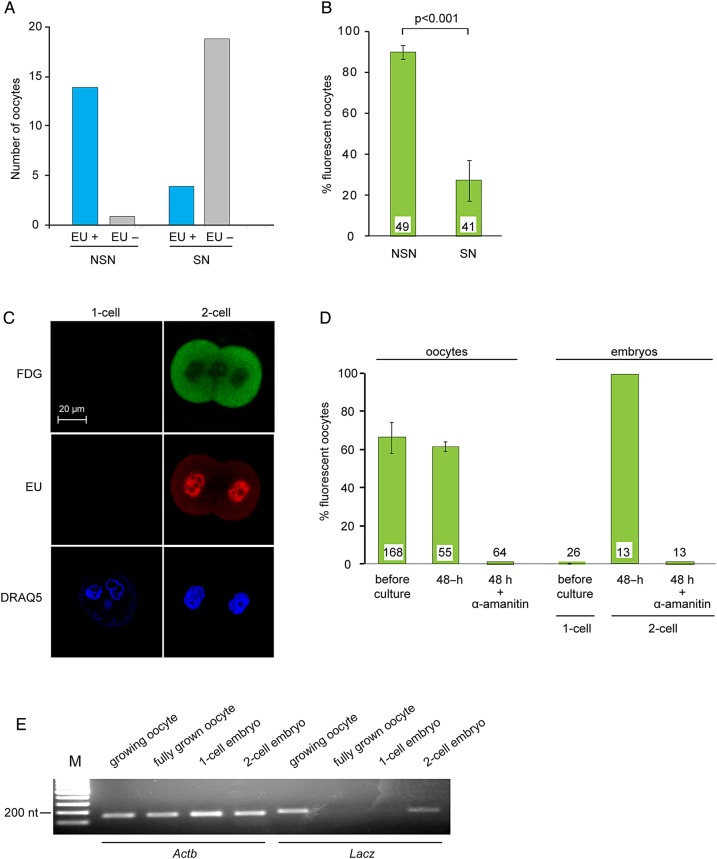
Figure 5.
Transcriptional regulation of β-galactosidase activity. (A) Oocytes within granulosa cell–oocyte complexes (GOCs) were incubated in the presence of EU to label newly synthesized RNA and then fixed and processed for EU detection and stained using DRAQ5 to assess chromatin configuration. Data are summed from four experiments. (B) Oocytes were stained using FDG to assess β-galactosidase activity and DRAQ5 to assess chromatin configuration. The experiment was performed three times. The number of oocytes examined is shown at the base of each bar. Two-sample t-test. (C) One-cell and two-cell embryos were incubated in the presence of EU and then processed to detect β-galactosidase activity (FDG) and RNA synthesis (EU). DNA was stained using DRAQ5. (D) Growing oocytes and one-cell embryos were stained using FDG. Other samples were then incubated in the absence or presence of α-amanitin for 48 h and then stained using FDG. The experiment was performed three times. The number of oocytes examined is shown at the base of each bar. (E) RNA was purified from oocytes and embryos at the indicated stages. RT-PCR was performed using primers corresponding to Actb and LacZ. The experiment was performed twice.