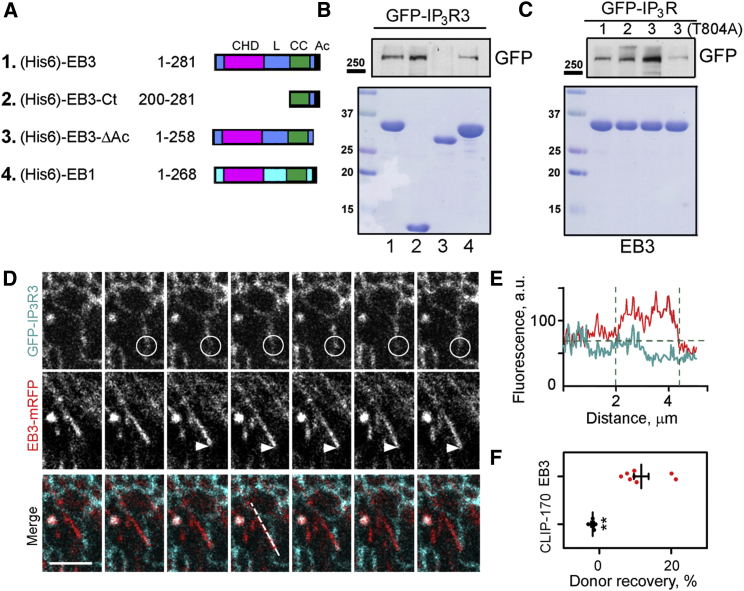
Figure 2.
EB3 Interacts Directly with IP3Rs
(A) Schematic representation of hexa-histidine (His6)-tagged EB constructs used for pull-down experiments. CHD, calponin homology domain; L, linker; CC, coiled coil; Ac, acidic tail.
(B and C) Pull-down analyses of interactions between (His6)-EB proteins covalently bound to Ni-NTA resin and lysates from HEK cells expressing GFP-IP3R1-3 or GFP-IP3R3(T804A). Upper panels show western blots for GFP and lower panels show Coomassie brilliant blue-stained gels loaded with 5% of the EBs (numbered as in A) used for the pull-down. Results are typical of three independent experiments. Western blots of GFP-IP3Rs in the cell lysates used and additional controls are shown in Figure S3.
(D) Confocal images collected at 850-ms intervals show simultaneous recordings of fluorescence from EB3-mRFP and GFP-IP3R3 in HLMVECs. The composite panels show overlaid GFP-IP3R3 (green) and EB3-mRFP (red). Note the loss of GFP-IP3R3 fluorescence (circle) as the EB3-mRFP-labeled microtubule tip approaches (arrow). Scale bar, 5 μm.
(E) EB3-mRFP and GFP-IP3R3 fluorescence recorded along the dashed line shown in the merged images in (D) illustrates the decrease in GFP fluorescence at the point of interaction with the microtubule tip.
(F) Focal photobleaching of the acceptor fluorophore (mRFP) at the microtubule tip while recording donor fluorescence from GFP-IP3R was used to assess the interaction between GFP-IP3R3 and EB3-mRFP or CLIP-170-mRFP at the microtubule tip. Individual data points with mean ± SEM from five to eight cells analyzed in each group show the recovery of the donor fluorescence after acceptor photobleaching (%). ∗∗Using Student’s t test.