Figure 1. NAD+ precursor metabolism and NAD+ consuming enzymes.
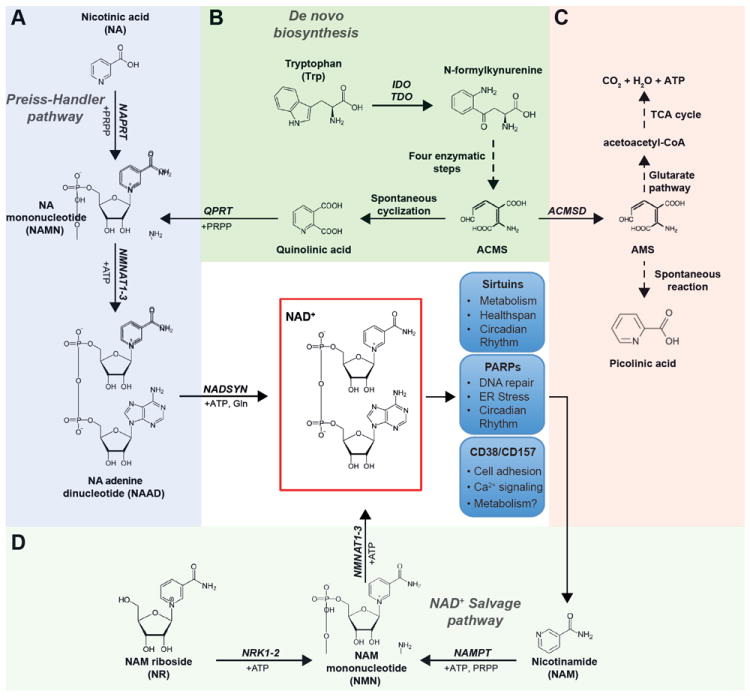
Tryptophan (Trp), nicotinic acid (NA), nicotinamide (NAM) and nicotinamide riboside (NR) are utilized through distinct metabolic pathways to form NAD+. A. NAD+ synthesis from NA, also known as the Preiss-Handler pathway, is initiated by the NA phosphoribosyltransferase (NAPRT), which uses phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) to form NAMN. Together with ATP, NAMN is then converted into NAAD by the NMN adenylyl transferase (NMNAT1-3) enzymes. Finally, NA adenine dinucleotide (NAAD) is transformed to NAD+ through an amidation reaction catalyzed by the NAD+ synthase (NADSYN) enzyme. B. The de novo biosynthesis of NAD+ from tryptophan (Trp) starts with the conversion of Trp to N-formylkynurenine by either indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) or tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO). After four reaction steps, N-formylkynurenine can be subsequently converted to the unstable α-amino-β-carboxymuconate-ε-semialdehyde (ACMS), which can undergo nonenzymatic cyclization to quinolinic acid. The last step of the de novo biosynthesis component is comprised of the quinolinate phosphoribosyltransferase (QPRT)-catalyzed formation of NAMN, using PRPP as a co-substrate, which is converted to NAD+ via the remaining pathway described in panel A. C. ACMS can also be diverted away from NAD+ synthesis, by ACMS decarboxylase (ACMSD), to form α-amino-β-muconate-ε-semialdehyde (AMS) and can then be oxidized via the glutarate pathway and TCA cycle to CO2 and water, or nonenzymatically converted to picolinic acid. D. The synthesis of NAD+ from NAM or NR is more direct and relies on only 2 steps each. NAM is converted by the rate-limiting nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) to form NMN, using PRPP as cosubstrate. NMN is also the product of phosphorylation of NR by the NR kinases (NRK1-2). The subsequent conversion of NMN to NAD+ is catalyzed by the NMNAT enzymes. The blue boxes depict the 3 families of NAD+ consuming enzymes and some of the key processes to which they have been linked. NMN, NAM mononucleotide; NAMN, NA mononucleotide; NAAD, NA adenine dinucleotide; NRK, NR kinase; NMNAT, NMN adenylyltransferase; NADSYN, NAD+ synthetase.
