Figure 2.
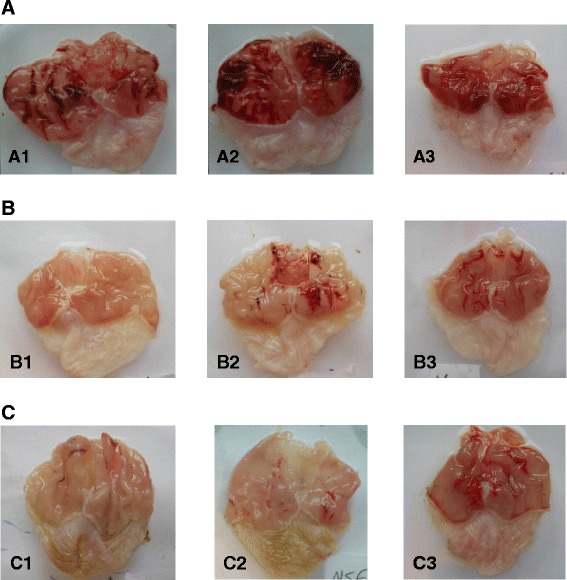
Gross examination of the gastric mucosa of rats treated with 10% DMSO-, CBX- or MEMM following pretreatment with saline, L-NAME or NEM, respectively. A. Gross examination of the gastric mucosa in rats. A1, A2 and A3 represent the control (10% DMSO) group pre-treated with saline, L-NAME (70 mg/kg) or NEM (10 mg/kg), respectively. Pre-treatment with L-NAME or NEM in control group aggravated the lesion formation as compared to saline pre-treated control group. B: Gross examination of the gastric mucosa in rats treated with CBX (100 mg/kg). B1, B2 and B3 represent the positive control group pre-treated with saline, L-NAME (70 mg/kg) or NEM (10 mg/kg), respectively. Pre-treatment with L-NAME or NEM in positive control group significantly reversed the gastroprotection activity of CBX.C: Gross examination of the gastric mucosa in rats treated with MEMM (500 mg/kg). C1, C2 and C3 represent the groups pre-treated with saline, L-NAME (70 mg/kg) or NEM (10 mg/kg), respectively. The gastroprotective effect exerted by MEMM against ethanol-induced damage was reversed by the pre-treatment of L-NAME or NEM, suggesting the involvement of nitric oxide and sulfhydryl compounds in the gastroprotection conferred by MEMM.
