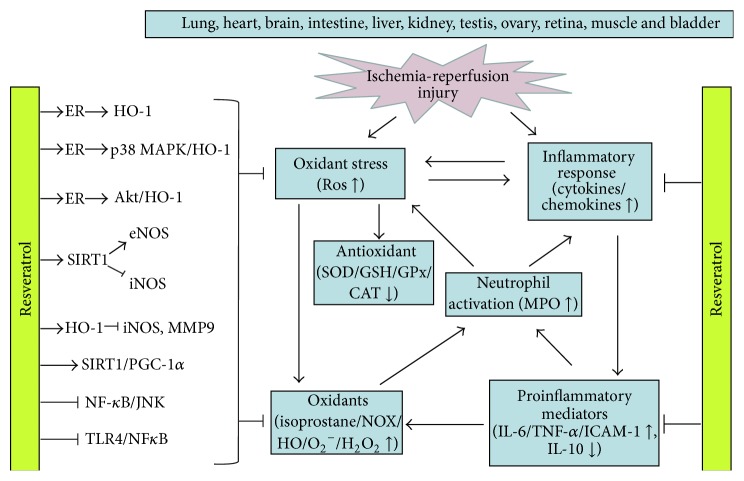
Figure 1.
The mechanisms and pathways of resveratrol in oxidative stress-mediated ischemia-reperfusion injury. The protective benefits of resveratrol involved are its scavenging, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effect and the signaling mechanisms mediated may be via a variety of intracellular signaling pathways, including upregulation of ER-related MAPK/HO-1 and Sirt1/PGC-1α pathway and inhibition of the TLR4 and NF-κB dependent pathway. ROS, reactive oxygen species; ER, estrogen receptor; HO-1, hemeoxygenase 1; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; p38 MAPK, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; MMP-9, metallopeptidase 9; SOD, superoxide dismutase; CAT, catalase; GSH, glutathione; GSH-Px, glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px); NOX, NADPH oxidase; XO, xanthine oxidase; O2 −, superoxide anions; HO−, hydroxyl free radicals; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-10, interleukin 10; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; MPO, myeloperoxidase.