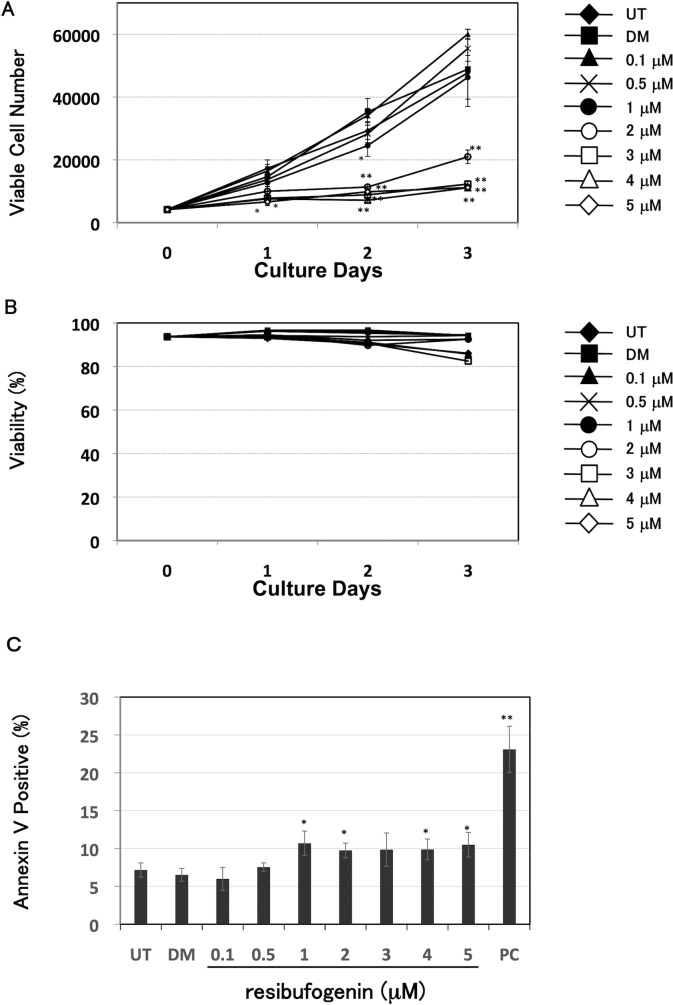
Fig 2. Resibufogenin inhibits the growth of human colon cancer HT-29 cells.
(A) Growth inhibitory effect of resibufogenin by counting viable cell number. Cells were treated with resibufogenin at the indicated concentrations for 1, 2, or 3 days. Viable cell number was measured by a Guava EasyCyte plus flow cytometry. UT, untreated; DM, treated with DMSO. Points, means (n = 3); bars, SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with the DMSO-treated control. (B) The effect of resibufogenin on cell viability. Cells were treated and measured as shown in (A). Viability was calculated using the number of viable cells and dead cells. UT, untreated; DM, treated with DMSO. Points, means (n = 3) (C) The effect of resibufogenin on apoptosis by annexin V staining. Cells were treated with resibufogenin at the indicated concentrations for 24 h, and subjected to annexin V staining. The stained cells were measured by FACSCalibur. UT, untreated; DM, treated with DMSO. Celecoxib at 100 μM was used as a positive control (PC). Points, means (n = 3); bars, SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with the DMSO-treated control.