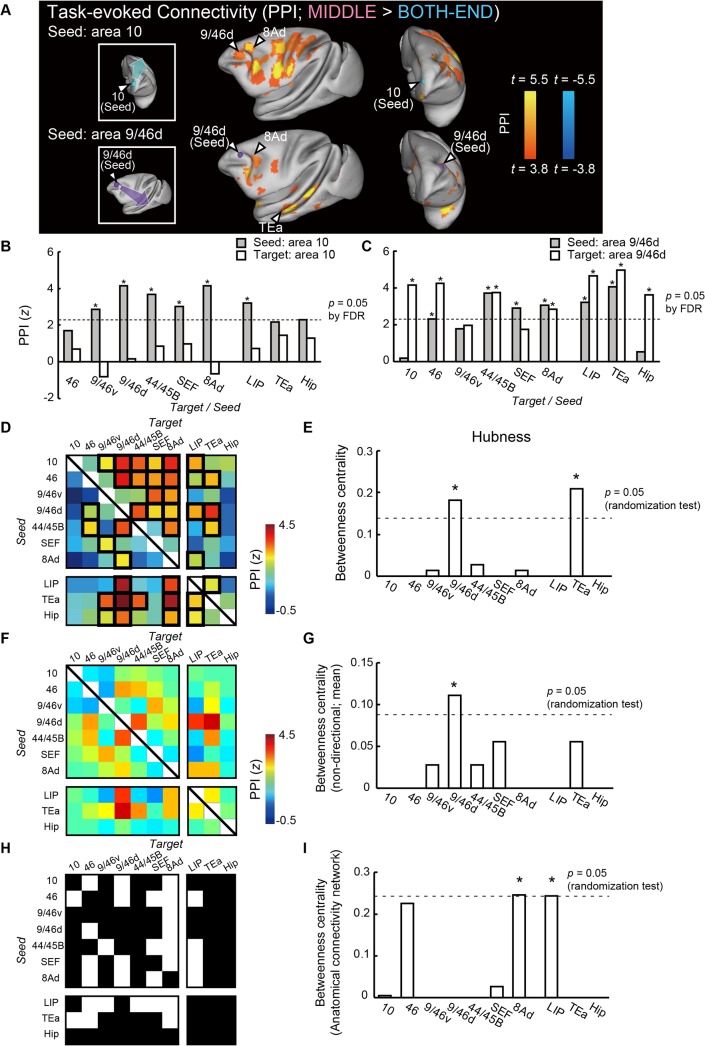
Fig 3. Hub-centric cortical network for temporal-order judgment.
(A) PPI (MIDDLE > BOTH-END). Color t-map of PPI is superimposed on the inflated brain. Upper and lower panels show the PPI maps for the seeds in areas 10 and 9/46d, respectively. (B, C) Two bar plots in each column show z-values for PPIs from area 10 (B) or area 9/46d (C) to other ipsilateral homotopic areas (gray) and PPIs from other homotopic areas to area 10 (B) or area 9/46d (C) (white). Dashed lines indicate significant z-value (p = 0.05 [FDR correction]). * p < 0.05 (FDR correction). (D) PPI matrix among the ten homotopic areas. Rows and columns indicate seed and target areas, respectively. Significant connectivities are enclosed by thick black lines (p < 0.05 [FDR correction]). (E) Betweenness centralities of each area calculated based on (D). The dashed line indicates the significance at p = 0.05 (randomization test [comparison with the distribution of the randomized network]). * p < 0.05. (F) PPI matrix among the ten homotopic areas without assumptions of directionality. The weight of the connection between A and B is evaluated as the mean value of PPIA->B and PPIB->A. (G) Betweenness centralities of each area calculated based on (F). The dashed line indicates significance at p = 0.05 (randomization test). * p < 0.05. (H) Anatomical connectivity matrix among the ten homotopic areas. Rows and columns indicate seed and target areas, respectively. A white (black) square indicates the presence (absence) of anatomical connection from row to column. Anatomical information is based on the CoCoMac database [41,47,48]. The projections to/from areas 8Ad, SEF, and LIP listed in the matrix are categorized as those to/from areas 8A, 6DR, and POa in CoCoMac, respectively. (I) Betweenness centralities of each area calculated based on (H). The dashed line indicates significance at p = 0.05 (randomization test). * p < 0.05.