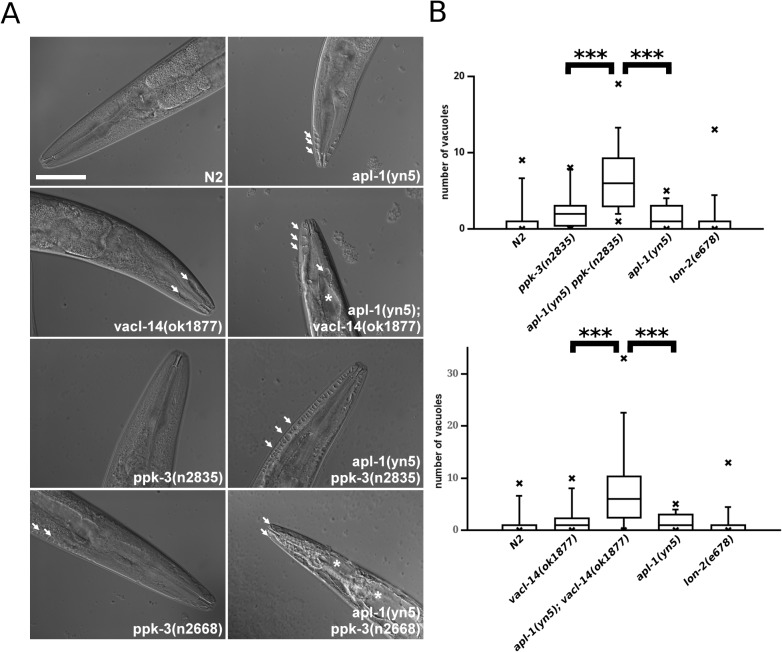
Fig 2. APL-1 interacts genetically with the PIKfyve complex genes vacl-14 and ppk-3.
(A) Mutations in apl-1, ppk-3 and vacl-14 led to the formation of vacuoles in the C. elegans intestine and hypoderm (indicated by arrows) apparent in the anterior tips of the worms as observed by Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) microscopy. Combination of apl-1, ppk-3 and vacl-14 mutations in double mutant worms strongly enhanced this phenotype (* indicate very large vacuoles), particularly evident in the apl-1(yn5) ppk-3(n2668) double mutant. (B) Box plots demonstrated that the number of vacuoles in apl-1/ppk-3 and apl-1/vacl-14 double mutants is significantly increased compared to the single mutants (Wilcoxon rank test, p<0.01, n≥20 per strain), demonstrating that APL-1 functionally interacts with the PPK-3 complex. This showed that the C-terminal domain of APL-1 is necessary for suppressing vacuole formation induced by loss of PPK-3 and VACL-14 activity. Bar, 50 μm.