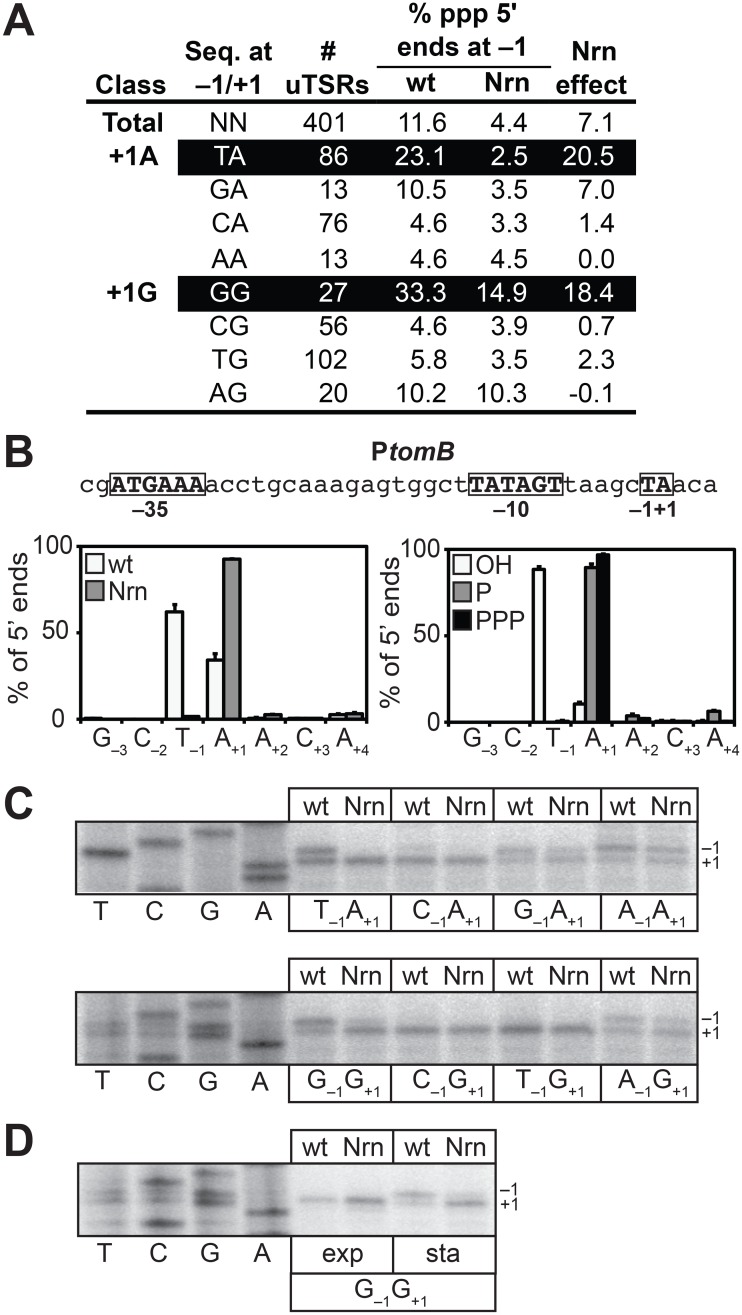
Fig 4. Detection of PDI in E. coli.
A. Analysis of PDI by 5′ RNA-seq. Percentage of transcripts emanating from position −1 of uTSRs with the indicated sequence at −1 and +1 in cells carrying wild-type concentrations of 2- to ~4-nt RNAs (wild-type) or cells in which the oligoRNase NrnB was ectopically expressed (Nrn). The Nrn effect represents the difference in these values. uTSRs with above average Nrn effect are highlighted in black. The total number of uTSRs used to calculate the percentages is indicated. Values are calculated from biological replicates listed in S8 Table. Data is derived from the analysis of all 5′ ends during stationary phase. B. Analysis of PDI at the promoter associated with tomB, ptomB, by 5′ RNA-seq. Sequence of ptomB is shown. Indicated are positions +1, −1 and the promoter −10 and −35 elements. Graph on the left shows average distribution of 5′ ends between positions −3 and +4 for ptomB in cells carrying wild-type concentrations of 2- to ~4-nt RNAs or cells in which the oligoRNase NrnB was ectopically expressed (Nrn) as detected by 5′ RNA-seq analysis of all 5′ ends during stationary phase. Graph on the right shows the average distribution of 5′ ends between positions −3 and +4 for ptomB in cells carrying wild-type concentrations of 2- to ~4-nt RNAs as detected by 5′ RNA-seq analysis of hydroxyl 5′ ends (OH), monophosphate 5′ ends (P), or triphosphate 5′ ends (PPP) during stationary phase. C. Primer extension analysis of plasmid-borne ptomB variants carrying the indicated sequence at −1 and +1 in cells carrying wild-type concentrations of 2- to ~4-nt RNAs (wt) or cells in which the oligoRNase NrnB was ectopically expressed (Nrn). D. Primer extension analysis of the plasmid-borne ptomB variant carrying the sequence G−1G+1 during exponential phase (exp) or stationary phase (sta).