Figure 1.
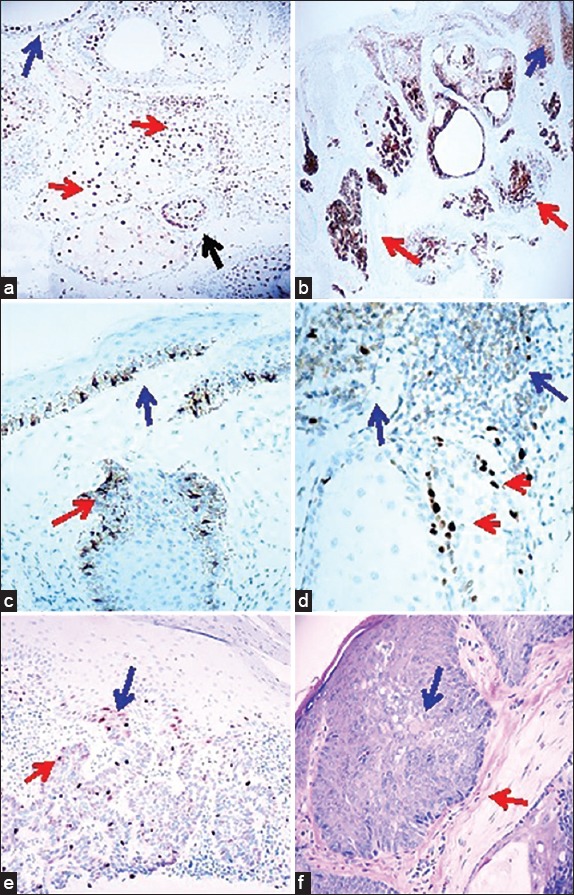
Immunohistochemical staining panel on sebaceoma. a. IHC, with P27Kip positive staining inside a tumor (brown staining; red arrows), and also in the adjacent epidermis above the tumor (brown staining; blue arrow) (100×) (the black arrows is positive around the tumor. b. IHC, demonstrating EMA/CD227 positive staining in a tumor (brown staining; red arrows) and also in the suprajacent epidermis (brown staining; blue arrow) (40×). c. IHC, demonstrating PCNA in the normal tissue above the tumor and in the bulb origin from the epidermis, positive staining inside a tumor palisade areas (brown staining; red arrow), and in the suprajacent epidermis (brown staining; blue arrow) (200×). d. IHC staining with Topoisomerase II, positive inside a tumor in palisaded areas (red arrow) and in surrounding peritumoral areas (brown staining; blue arrow) (400×). e. Cyclin D1 IHC staining, positive in palisaded areas of a tumor (brown staining; red arrow) as well as in an area where the tumor seems to be originating from the epidermis (brown staining; blue arrow) f. H&E staining of a tumor demonstrates focal features of BCC, with the palisaded areas (red arrow) and sebaceous differentiation areas (blue arrow).
