Figure 2.
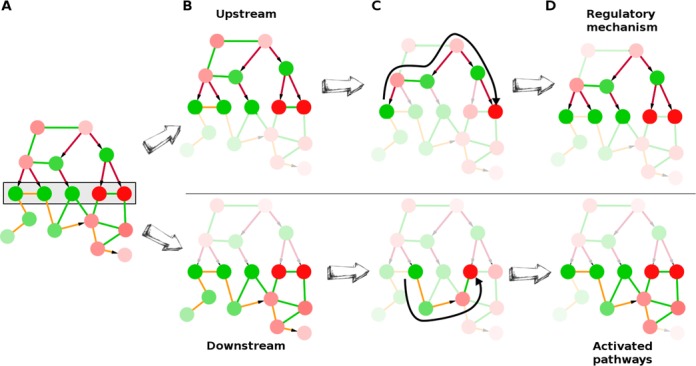
Conceptual representation of the sub-network inference by PheNetic. The colors of the edges indicate the different types of interactions with green referring to protein–protein, red to protein–DNA and orange to metabolic interactions. Arrows indicate the direction of the interaction. PheNetic will infer the sub-network from the interaction network that best connects the genes from a gene list (A, gray box), given the differential expression data. PheNetic can be used in two different run modes: the upstream run mode (B top) and the downstream run mode (B, bottom). To infer the upstream regulatory sub-network (C, top), paths (thick black arrow) between the genes of the gene list should first run upstream, against the natural direction of the interaction network, and then run downstream, following the natural direction of the interaction network. In addition to this, both the terminal edges of the path have to be regulatory interactions (e.g. DNA–Protein, sRNA, …). To infer the activated downstream pathways (C, bottom), paths between the genes of the gene list run downstream, hereby following the natural direction of the network. By selecting the smallest sub-network that best connects the genes from the gene list given the specific run mode, PheNetic is able to select the regulatory mechanisms responsible for the observed expression (D, top) or on the pathways/protein complexes that are differentially expressed or that result in the observed differential expression (D, bottom).
