Figure 4.
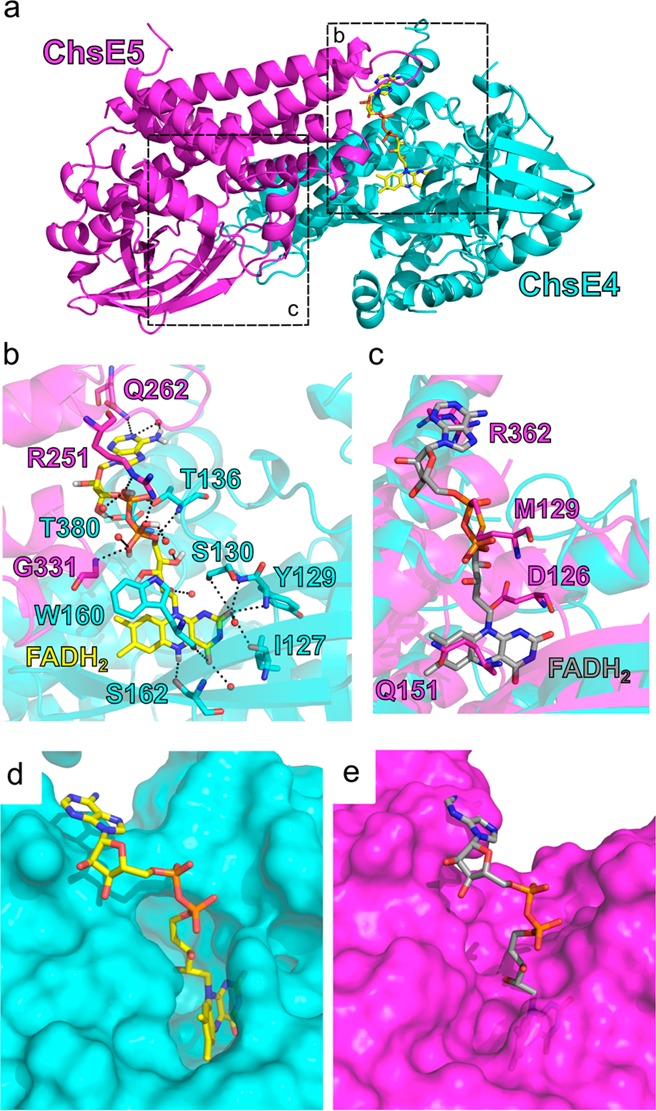
FAD binding sites. (a) There is only one FAD cofactor per ChsE4-ChsE5 dimer. The FAD cofactor binds at the interface of the ChsE4 and ChsE5 chains. The actual FAD binding site is in box b, and the nonfunctional FAD binding region is in box c. (b) The detailed hydrogen bonding network that stabilizes bound FAD is shown. FAD is colored yellow. Water molecules are shown as red balls. Hydrogen bonding interactions are shown as black dashes. Residues that interact with FAD are labeled. The isoalloxazine ring is located inside ChsE4, and both ChsE4 and ChsE5 stabilize adenine. (c) The region in ChsE5 equivalent to the FAD binding site in ChsE4 is shown after superimposing ChsE5 onto ChsE4/FAD. The FAD molecule bound to ChsE4 is shown in gray, and residues from ChsE5 that would clash with FAD are shown and labeled. (d) Surface representation of the actual FAD binding site in ChsE4. Protein chains are shown on the surface, and the FAD molecule is colored in yellow and represented by sticks. (e) Surface representation of the nonfunctional FAD binding region in ChsE5. The FAD molecule is colored in gray.
