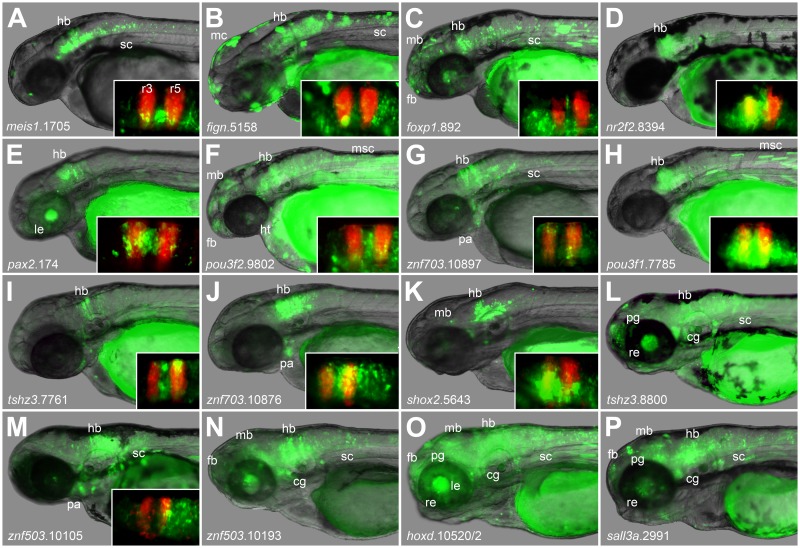
Fig 3. Conserved PBX-HOX and MEIS/PREP motifs predict hindbrain enhancers accurately.
Images show expression driven during transient transgenic assays (see methods) between 2 and 3 dpf. Insets show comparison with RFP in rhombomeres 3 and 5. Constructs drive expression in hindbrain and in other tissues meis1.1705 (A) in hindbrain and spinal cord; fign.5158 (B) in hindbrain, spinal cord and melanocytes; foxp1.892 (C) in the central nervous system; nr2f2.8394 (D) in hindbrain; pax2.174 (E) in hindbrain and lens; pou3f2.9802 (F) in the central nervous system, heart and muscle; znf703.10897 (G) in hindbrain, spinal cord and pharyngeal arches/neural crest; pou3f1.7785 (H) in hindbrain; tshz3.1.7761 (I) in hindbrain; znf703.10876 (J) in hindbrain and pharyngeal arches/neural crest; shox2.5643 (K) in hindbrain; tshz1.8800 (L) in hindbrain, spinal cord, retina, pineal gland and cranial ganglia; znf503.10105 (M) in hindbrain, spinal cord and pharyngeal arches; znf503.10193 (N) in the central nervous system and cranial ganglia; hoxd.10520/1 (O) in the central nervous system, lens, retina, pineal gland and cranial ganglia; and sall3a.2991 (P) in the central nervous system, retina, pineal gland and cranial ganglia. fb: forebrain; mb: midbrain; hb: hindbrain; sc: spinal cord; pa: pharyngeal arches/neural crest; cg: cranial ganglia; mc: melanocytes; msc: trunk muscle cells; le: lens; re: retina; pg: pineal gland.