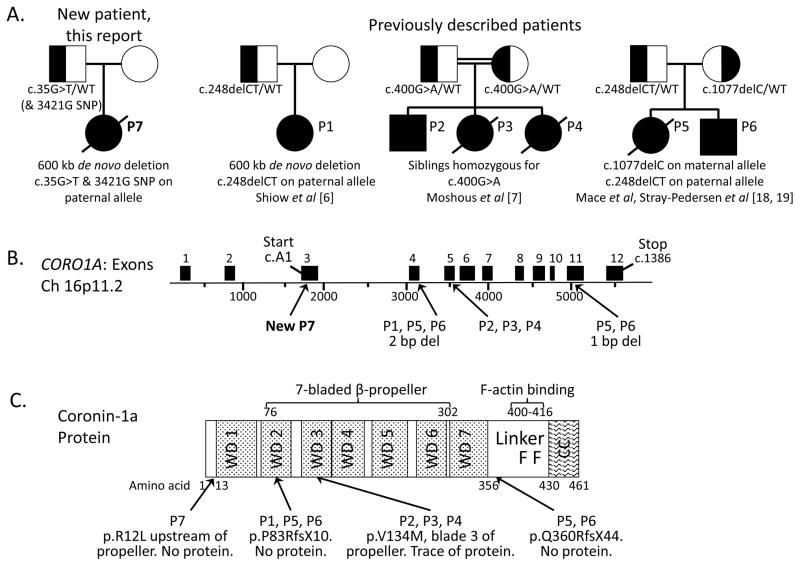
Figure 1.
A, Pedigrees of 4 families reported to date with CORO1A deficiency. Left: new patient P7; previously described patients are shown in order of publication. Note while Moshous et al [7] used mutation numbering 717G>A for P2, P3 and P4 corresponding to CORO1A transcript variant 2, NM_007074.3, we list all mutations here using the initial A of the first translated codon ATG as cDNA1 (variant 1, NM_001193333), per Shiow et al [6].
B, CORO1A gene locus indicating transcript NM_001193333 and positions of known disease-causing mutations.
C, Major structural domains of Coronin-1A protein, indicating mutation sites. WD, tryptophan-asparagine repeat region; linker domain, aa 356–429 containing positively charged residues 400–416 forming 2 F-actin binding sites [24]; CC, coiled-coil domain, aa 430–461, required for homo-trimerization.