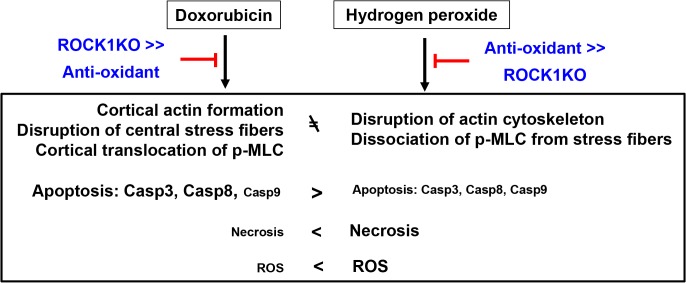
Fig 10. Schematic summary.
The diagram summarizes the effects of antioxidant (NAC) and ROCK1 deficiency in opposing apoptosis, necrosis, ROS production and actin cytoskeleton alterations induced by H2O2 and doxorubicin. Antioxidant treatment shows a stronger protection than ROCK1 deletion against H2O2-induced cytotoxic effects while ROCK1 deletion shows a stronger protection than antioxidant treatment against doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity. These results support the notion that doxorubicin induces apoptosis, necrosis, and actin cytoskeleton alterations predominantly through a ROS-independent and ROCK1-dependent mechanisms. Additional results supporting this concept include different temporal patterns and magnitudes of caspase activations and necrotic cell death, different levels of ROS production and different alteration of actin cytoskeleton induced by H2O2 compared to doxorubicin.