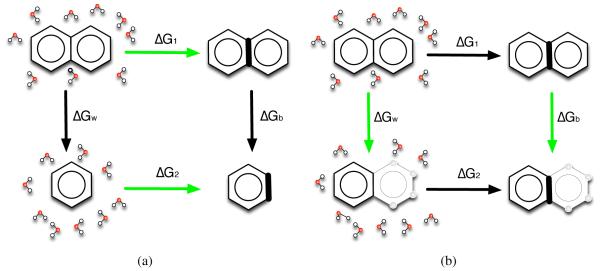
Figure 6.
The calculations we run are the green arrows. (a) We calculate the absolute “binding” free energy for each molecule, green arrows shown in (a), from water to the hypothetical binding site and then get the difference in absolute binding free energies as ΔΔGab = ΔG1 − ΔG2. Since in this case ΔG1 + ΔGb− ΔG2 − ΔGw = 0, then ΔΔGab = ΔGw − ΔGb. (b) We also calculate the relative “binding” free energy, green arrows shown in (b), by changing atoms to dummy atoms (hollow spheres), and get the relative binding free energy difference as ΔΔGrl = ΔGw − ΔGb. Here the bold bond on the right hand side of both panels represents the bond strained by “binding” to our hypothetical receptor (here represented by introducing restraints).