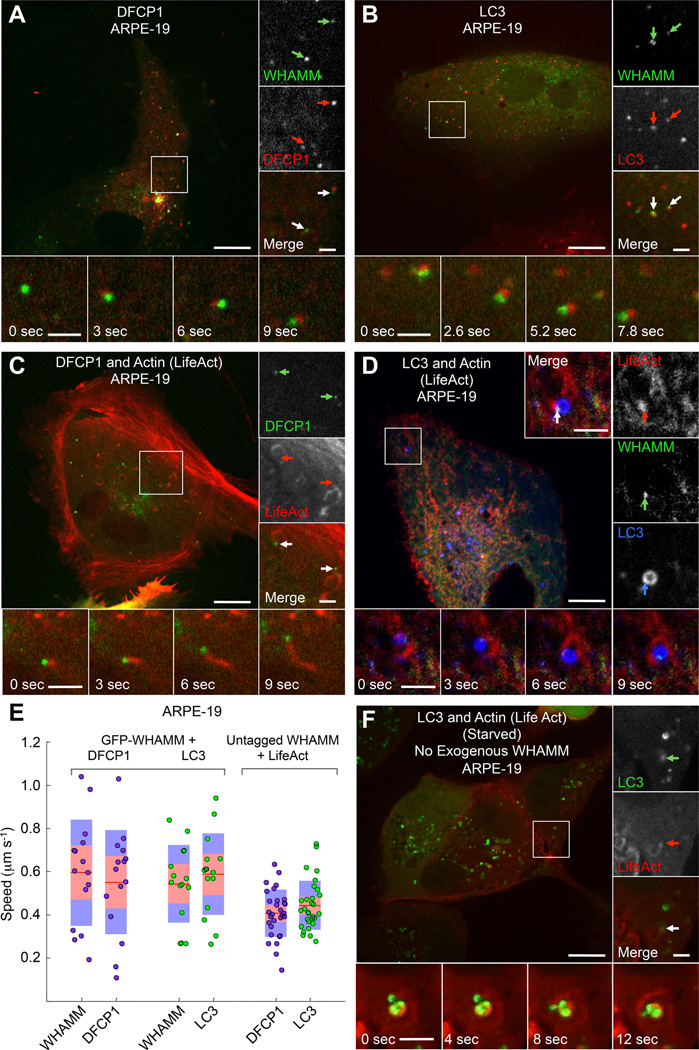
Figure 2. WHAMM-Dependent Comet Tails Propel the Movement of the Autophagosome Markers DFCP1 and LC3.
(A) GFP-WHAMM puncta comigrate with puncta of the omegasome marker mCherry-DFCP1 in fed ARPE-19 cells (color-coded arrows).
(B) GFP-WHAMM puncta comigrate with puncta of the autophagosome marker mCherry-LC3 in fed ARPE-19 cells.
(C) DFCP1 puncta are propelled by actin comet tails in ARPE-19 cells cotransfected with GFP-DFCP1, untagged WHAMM, and mCherry-LifeAct. Insets show two DFCP1 puncta (green arrows) with trailing actin comet tails (red arrows).
(D) WHAMM forms discrete puncta on LC3-coated vesicles (autophagosomes) that are propelled by actin comet tails in cells cotransfected with GFP-WHAMM, BFP2-LifeAct (red), and mCherry-LC3 (blue) in a fed ARPE-19 cell. Insets show a WHAMM punctum (green arrow) attached to an LC3 vesicle (blue arrow) and leading an actin comet tail (red arrow).
(E) Quantification of puncta speed for the indicated markers (n=30 puncta from 5 cells expressing GFP-WHAMM, and n=20 for 3 cells expressing untagged WHAMM).
(F) LC3 positive vesicles colocalize with actin-dense comet tails, which propel their movement in starved ARPE-19 cells expressing GFP-LC3 and mCherry-LifeAct but not exogenous WHAMM.
Scale bars in whole cell and inset images are 10 and 2 µm, respectively.