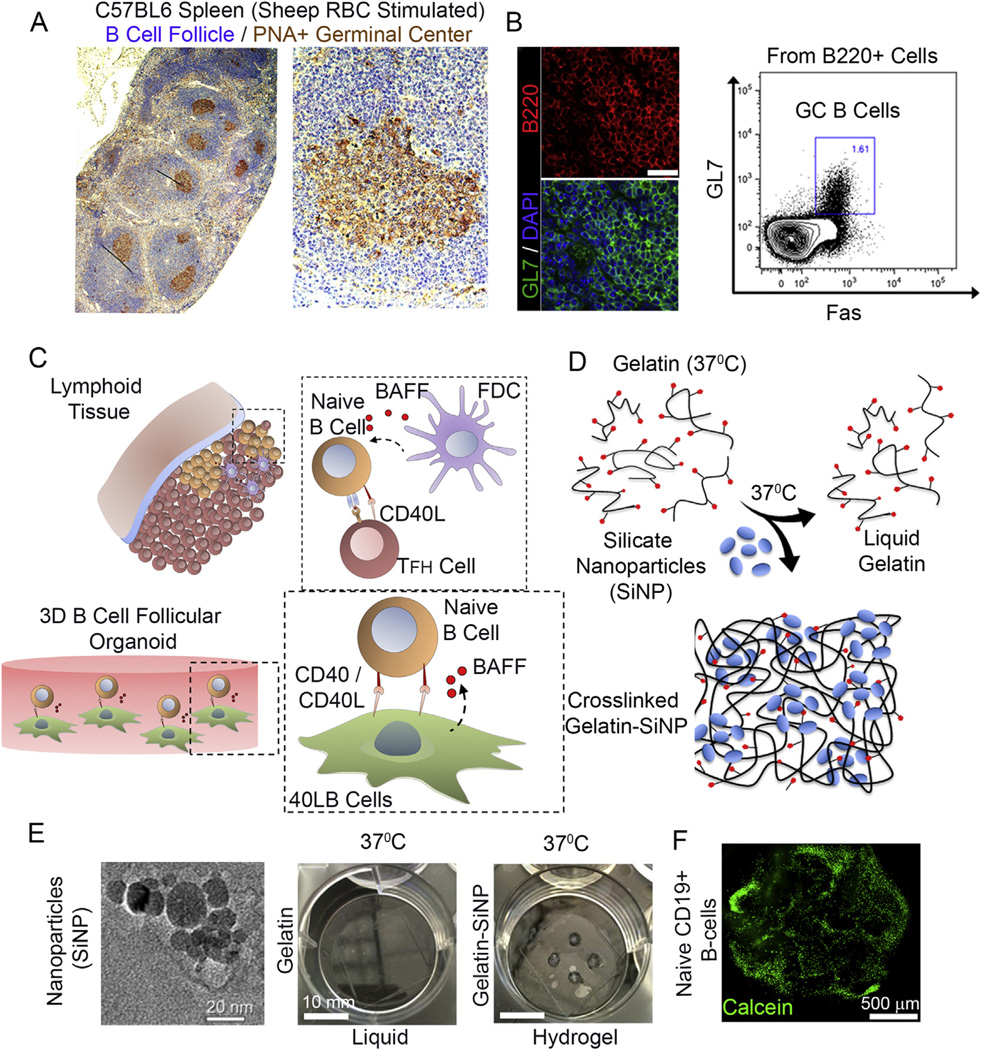
Fig. 1.
Ex vivo engineered B cell follicle organoid. (A) Immunohistochemical analysis of a spleen stained for H&E and GC marker peanut agglutinin (PNA). Right panel represents immunofluorecnece images of splenic tissue stained with GC marker GL7; scale bar 50 µm. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of B220+ primary B cells from immunized C57BL6 mice with the gate indicating GL7+Fas+ GC B cell population. (C) Schematic of the in vivo interaction between mature naïve B cells with follicular T helper (Tfh) cells and follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) within the lymphoid tissue follicle. FDCs produce B cell activation factor (BAFF) that support naïve B cell activation and conversion to germinal center phenotype. (D) Overview on the use of silicate nanoparticles (SiNP) for ionic crosslinking of gelatin to form stable hydrogel at 37 °C. (E) TEM of silicate nanoparticles (Left, scale bar 20 nm). Hydrogels composed of gelatin only and those ionically cross-linked with SiNP were compared for gelation at 37 ° C (Right, scale bar 10 mm). (F) Primary B cell viability and distribution 24 h following the encapsulation procedure (Bottom; green: Calcein; scale bar 500 µm). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)