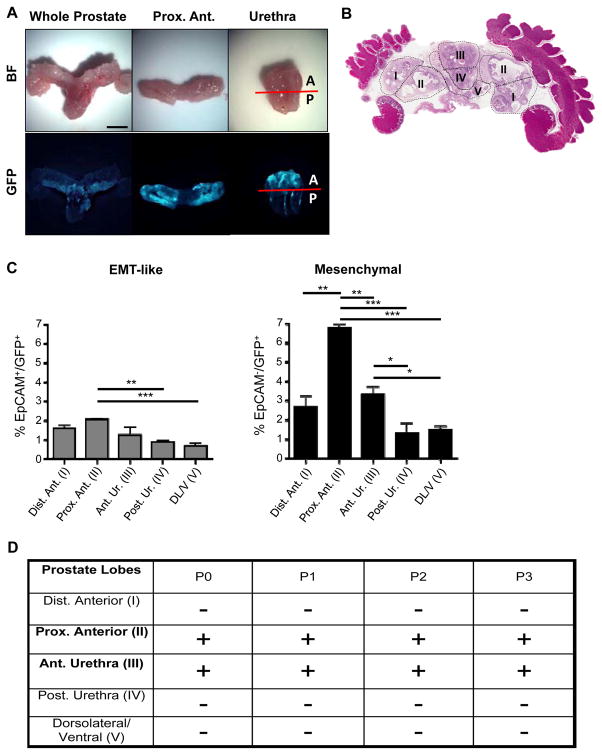
Figure 3.
Prostate regions enriched in Vim-GFP+ cells are able to regenerate transplantable tumors in vivo. A, Bright-field (BF) and fluorescent images of a whole-mount CPKV prostate (10 weeks). GFP expression in CPKV prostates is most prominent in the proximal region of the anterior lobes and in the anterior portion of the urethra. B, Diagram depicting how prostate regions/lobes were separated. I, distal region of the anterior lobe. II, proximal region of the anterior lobe. III, anterior portion of the urethra. IV, posterior portion of the urethra. V, dorsolateral/ventral lobes. C, FACS analysis demonstrates that the anterior portion of the urethra and proximal region of the anterior lobes express the highest percentage of mesenchymal cells compared to other regions/lobes from the prostates of CPKV mice (10–12 weeks). The percentage of EMT tumor cells was also slightly higher in the proximal region of the anterior lobes compared to other lobes/regions. D, The only CPKV prostate regions/lobes that produced transplantable tumors in NSG mice were the proximal region of the anterior lobe and anterior portion of the urethra. Data in C are represented as mean ± SEM. Bar, 4mm. A, anterior. P, posterior. Dist. Ant., distal region of the anterior lobe. Prox. Ant., proximal region of the anterior lobe. Ant. Ur., anterior portion of the urethra. Post. Ur., posterior portion of the urethra. DL/V, dorsolateral/ventral lobes. P0, passage 0. P1, passage 1. P2, passage 2. P3, passage 3. +, tumor. −, no tumor. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01. ***, P < 0.001.