Fig. 8.
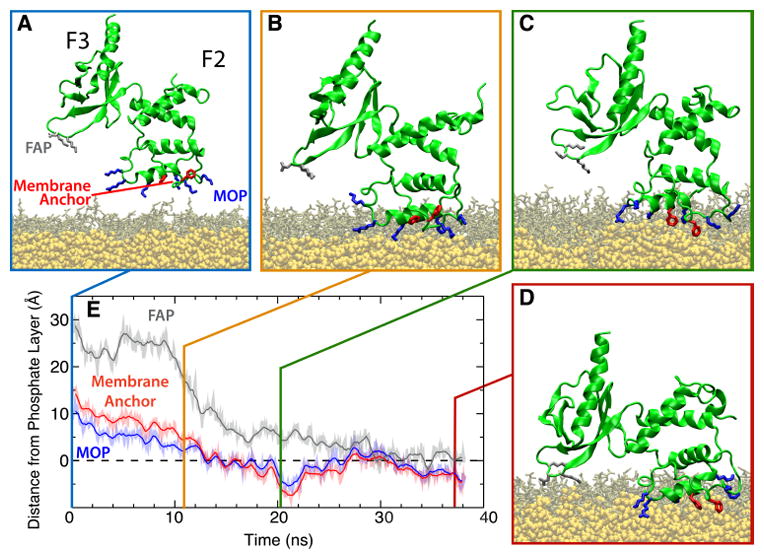
Membrane-binding sequence of the talin F2F3 subdomain. (A) Initial configuration of the talin F2F3 subdomain (green) in the PS HMMM system (DVPS, brown; DCLE, yellow). Residues comprising the MOP (blue), FAP (gray), and Phe-rich membrane anchor (red) are shown. In all images, water and ions have been omitted for clarity. (B–D) The three distinct stages of talin binding to the membrane are demonstrated. Talin is initially attracted to the membrane via MOP residues (B), followed by insertion of the Phe-rich membrane anchor (C), and, finally, a large, interdomain conformational change that brings the F3 subdomain into contact with the membrane surface (D). (E) Timeseries of the height of the MOP, FAP, and Phe-rich membrane anchor with reference to the phosphate layer of the cis leaflet (dashed line) from a representative membrane-binding simulation are shown. See Arcario and Tajkhorshid (2014) for data on all five independent simulations.
