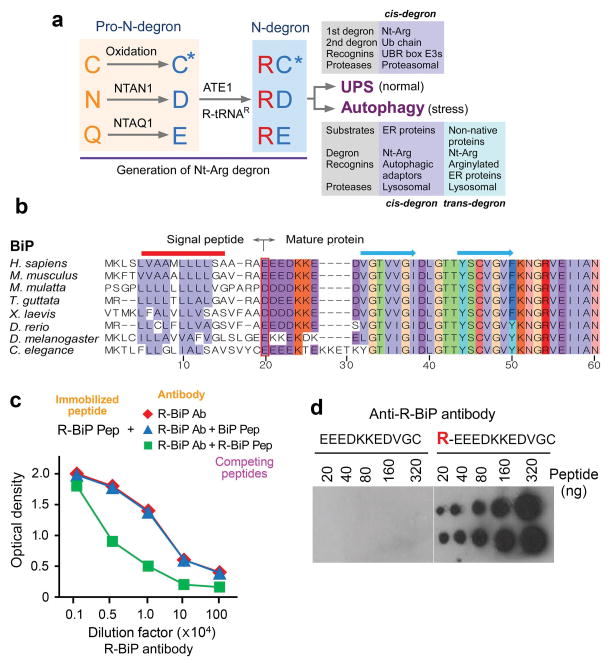
Figure 1.
Bioinformatic analysis of the ER N-end rule pathway, and the generation of antibodies to the arginylated form of the ER chaperone BiP. (a) A summary of this study that describes a dual role for the Nt-Arg residue as a degron for both the UPS and autophagy. The Nt-Arg residue generated through the N-end rule pathway is known to act as a degron for selective proteolysis by the UPS. In the Ub-dependent N-end rule pathway, specific recognition components, called N-recognins, recognize and bind the primary degron Nt-Arg and mediate ubiquitination for targeting to the proteasome. The results of this study show that N-terminal arginylation of ER-residing chaperons generates a cis-acting delivery determinant and degron for lysosomal degradation along with associated cargoes. In this autophagic proteolysis, Nt-Arg of BiP and other ER proteins is recognized by a recognin, the autophagic adaptor p62. The binding of Nt-Arg to p62 activates p62, leading to the delivery of p62, R-BiP, and its cargoes to autophagosomes. In definition, Nt-Arg also acts as a trans-acting degron for its cargoes. (b) A sequence alignment of the N-terminal regions of human BiP and its sequelogs. The red box indicates the N-terminal residues (P1′ sites) of mature BiP proteins from various species. Shown above are secondary structures (solid line, αhelices; arrows, βstrands). (c) Generation of anti-R-BiP DH1 antibody. Shown is a peptide binding/competition assay. An 11-mer R-BiP peptide (R-BiP-peptide) corresponding to the N-terminal region of R-BiP was immobilized on a 96-well plate, followed by incubation with serially diluted anti-R-BiP antibody and, subsequently, anti-goat secondary antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxide. The amounts of R-BiP antibody that bound to immobilized R-BiP peptide were determined based on O.D. value at 450 nm of secondary antibody. As a control, BiP-peptide, a 10-mer peptide corresponding to the N-terminal region of unarginylated BiP, was used. (d) A dot blotting analysis of R-BiP antibody using the peptides corresponding to the N-terminal region of unarginylated (left) or arginylated (right) BiP.