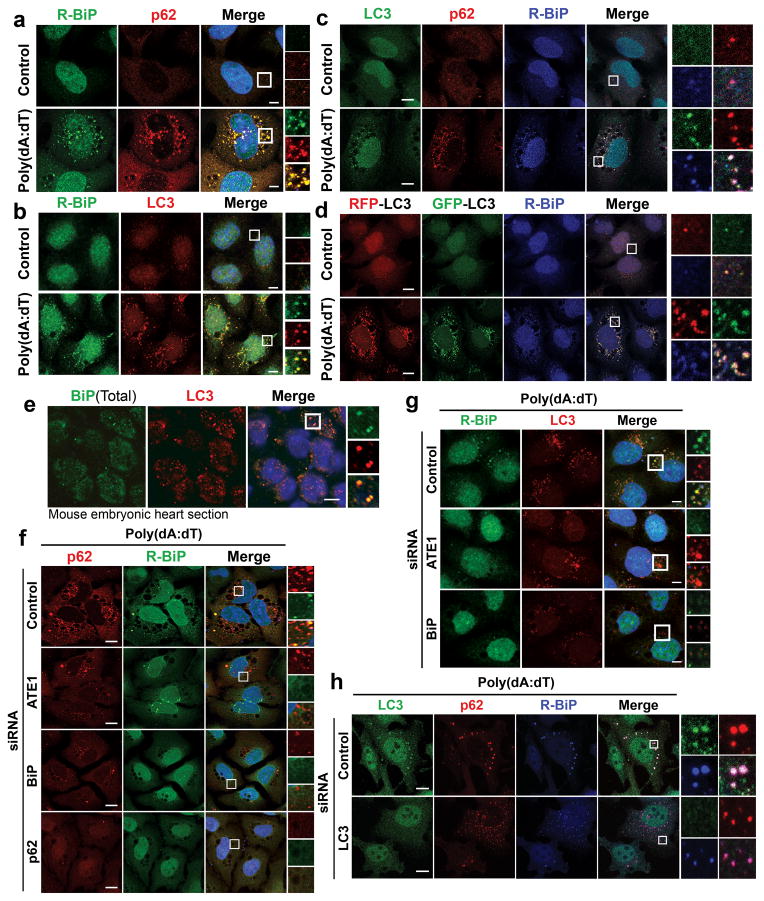
Figure 3.
R-BiP is targeted to the autophagosome via p62 bodies. Scale bars, 10 μm. (a) Colocalization of cytoplasmic R-BiP puncta with p62 puncta in poly(dA:dT)-treated HeLa cells. (b) Colocalization of R-BiP puncta with LC3 puncta in HeLa cells stably expressing RFP-GFP-LC3 as determined by immunostaining of R-BiP in comparison with RFP signal (red) which represents LC3-positive autophagic vacuoles. (c) Three color colocalization analysis between R-BiP (blue), p62 (red), and LC3 (green) in poly(dA:dT)-treated HeLa cells. (d) HeLa cells expressing RFP-GFP-LC3 were subjected to three color colocalization analysis between R-BiP (blue), acid-resistant RFP (red), and acid-sensitive GFP (green). Most R-BiP puncta show a strong colocalization with LC3 puncta which are positive for both RFP and GFP, indicating the delivery of R-BiP to autophagosomes. (e) Immunohistochemistry of total BiP and LC3 on sections of mouse embryonic hearts at embryonic day 13.5, which reveals BiP puncta that colocalize with LC3 puncta. (f) RNA interference assay of ATE1, BiP, and p62 in poly(dA:dT)-treated HeLa cells, followed by colocalization analysis between R-BiP and p62. Note that knockdown of any of ATE1, BiP, and p62 disrupts the targeting of both R-BiP and p62 to autophagic vacuoles. (g) RNA interference assay of ATE1 and BiP in poly(dA:dT)-treated HeLa cells expressing RFP-GFP-LC3, followed by colocalization analysis between R-BiP and LC3. (h) RNA interference assay of LC3 in poly(dA:dT)-treated HeLa cells, followed by colocalization analysis between R-BiP, p62, and LC3. LC3-knockdown apparently did not affect significantly the delivery of R-BiP to p62 puncta.