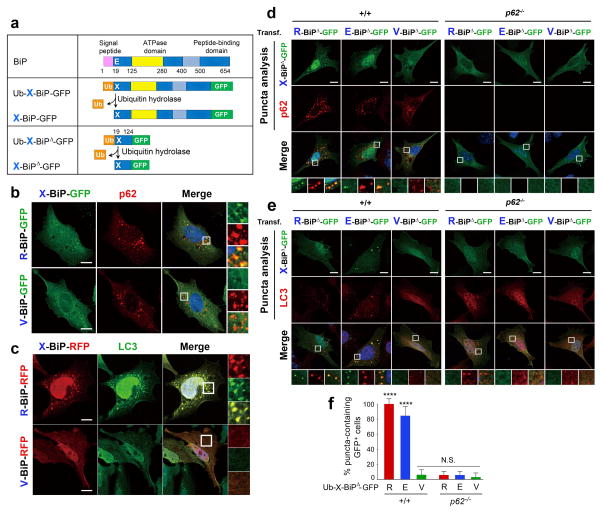
Figure 4.
The Nt-Arg residue of R-Bip is a delivery determinant to the autophagosome. (a) A schematic diagram showing that the Ub fusion protein Ub-X-BiP-GFP is cotranslationally cleaved into Ub and X-BiP-GFP by Ub hydrolases. Also shown is how Ub-X-BiP19–124-GFP (Ub-X-BiPΔ-GFP) is cotranslationally cleaved into Ub and X-BiPΔ-GFP. (b) Colocalization analysis between X-BiP-GFP (X= Arg (an arginylated form of Glu-BiP, Arg-Glu-BiP) or Val (a Glu-to-Val mutant, Val-BiP-GFP)) and p62 in HeLa cells. X-BiP-GFP is produced in vivo from a precursor protein, Ub-X-BiP-GFP, which is elaborated in a. Scale bar, 10 μm. (c) An analogous colocalization assay with X-BiP-RFP and LC3. Scale bar, 10 μm. (d) Puncta colocalization analysis of X-BiP19–124-GFP (X-BiPΔ-GFP; X= Arg, Glu, and Val) and p62 in +/+ and p62−/− MEFs. Note that the ability of X-BiPΔ-GFP to form cytosolic puncta not only follows the N-end rule but also requires p62. Scale bar, 10 μm. (e) Puncta colocalization analysis of X-BiPΔ-GFP and LC3 in +/+ and p62−/− MEFs, which shows that the colocalization of R-BiP puncta with LC3 depends on both the N-end rule and p62. Scale bar, 10 μm. (f) Quantitation of d and e indicating that the ability of R-BiP to form cytosolic puncta depends on p62. The graph shows the percentage of BiPΔ-GFP-positive cells that form BiPΔ-GFP punta. Mean +/− s.d. of n=3 independent experiments in which 200 cells were analysed per experimental point. Statistical significance was calculated using a one-way ANOVA test (N.S. p > 0.05; **** p < 0.0001).