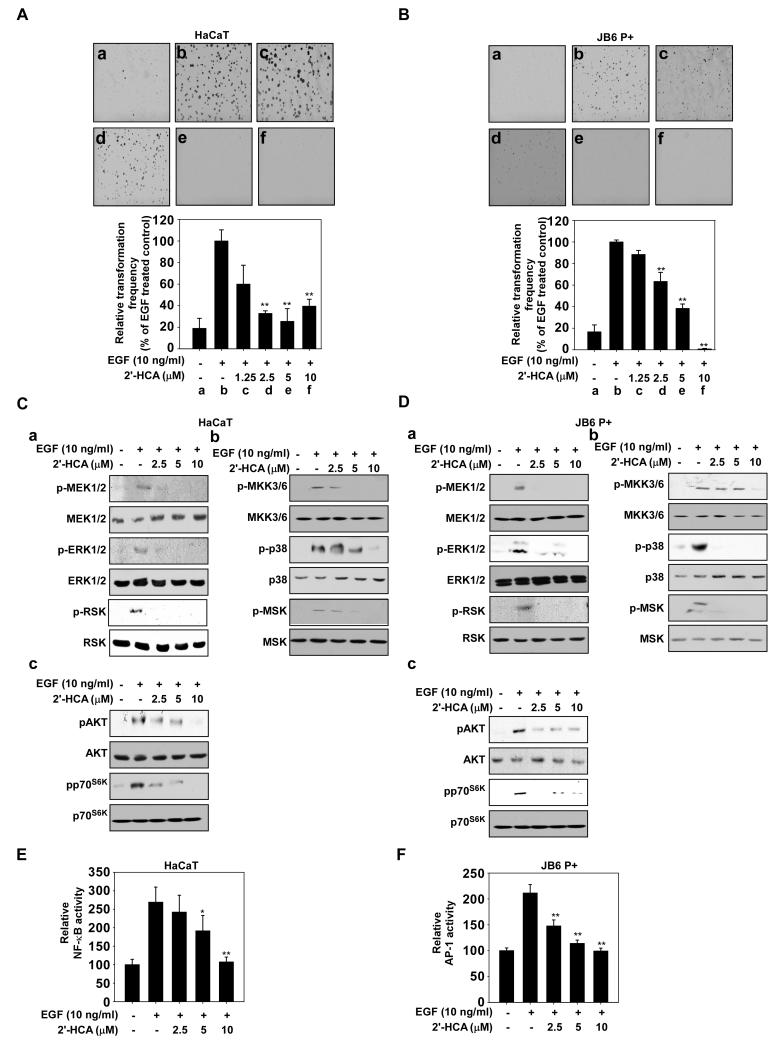
Figure 3.
2′-HCA inhibits epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced neoplastic transformation of HaCaT and JB6 P+ cells. 2′-HCA inhibits EGF-induced neoplastic transformation of (A) HaCaT and (B) JB6 P+ cells. The effect of 2′-HCA on EGF-induced cell transformation compared with untreated control cells (a); and cells treated with EGF alone (b); EGF and 1.25 μM 2′-HCA (c); EGF and 2.5 μM 2′-HCA (d); or EGF and 5 μM 2′-HCA (e); or EGF and 10 μM 2′-HCA (f). The colonies were counted under a microscope with the aid of the Image-Pro Plus software program (vs. 6.2). Results are represented as mean values ± S.E. (n = 3). The asterisks (*, **) indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05, p < 0.01) compared with the EGF-treated group. 2′-HCA inhibits ERK1/2, p38 and AKT signaling in (C) HaCaT and (D) JB6 P+ cells. HaCaT or JB6 P+ cells were treated with 2′-HCA (0, 2.5, 5, or 10 μM) for 1 h before treatment with EGF (10 ng/mL) and then harvested after 15 min. Immunoblot analysis was conducted as described in Materials and Methods. 2′-HCA suppresses EGF-induced (E) NF-κB and (F) AP-1 transactivation. JB6 P+ cells, which were stably transfected with NF-κB or AP-1 luciferase reporter plasmids, were pretreated with 2′-HCA (0, 2.5, 5, or 10 μM) for 1 h before being exposed to EGF (10 ng/ml) and harvested 6 h later. Relative luciferase activities were determined and data are presented as mean values ± S.D. The asterisks (*, **) indicate a significant (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01) inhibition of luciferase activity by 2′-HCA compared to the group treated with EGF alone.