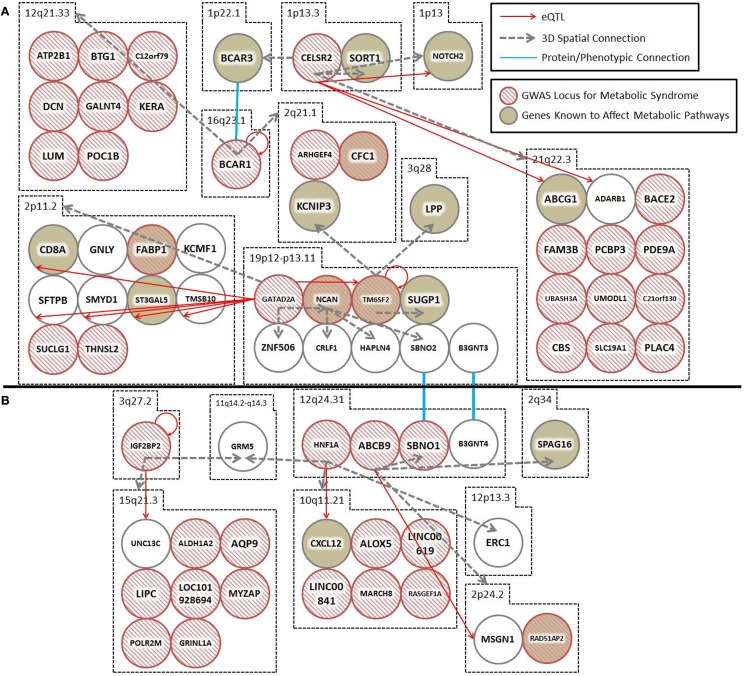
Figure 1.
Spatial and trans-expression Quantitative Trait Loci (trans-eQTL) connect diabetes loci from different GWAS meta-analyses. Spatial connections (dashed gray arrows) were obtained from data within the ENCODE database, focusing on those loci that recent meta-analyses have verified as being associated with diabetes. Spatial connections link loci together into a hub(s). These hubs might (1) be regulatory (i.e., contribute to the regulation of nuclear processes including gene regulation, DNA repair, and DNA replication); (2) structural; or (3) simply the result of random associations. To test the hypothesis that some of these spatial connections are regulatory, we included a trans-eQTL analysis (red arrows). The trans-eQTL analysis highlights significant expression effects associated with the GWAS loci within the spatially associated loci. The eQTL data were derived from a single cancer cell line in the eight Hapmap populations. Future work should determine if these eQTL results are replicated in pancreatic or cardiac cells from individuals developing symptoms of the metabolic syndrome (data currently unavailable). Loci that were identified by GWAS as being important for T2D and the metabolic syndrome are represented by hashed red circles. Loci in biological pathways related to T2D or metabolic syndrome are represented by tan filled loci. Protein/phenotype connections (blue lines) are illustrated where appropriate to connect relevant loci and further expand the regulatory co-interaction diagram. For example, (1) spatial associations with KCNIP3 (2q21) and a physical connection between the BCAR1–BCAR3 proteins link TM6SF2, CTRB1–BCAR1, and CELSR2–PSRC1, into a spatial hub and (2) GRM (11q14) links the IGF2BP2 locus (3q27) to the HNF1A locus (12q24) together along with other loci that have been previously implicated in diabetes. (A,B) illustrate two spatial hubs that are connected by functional linkages between SBNO1-SBNO2 and B3GNT3-BGNT4. *For the sake of clarity, the following loci were abbreviated: CELSR2, CELSR2/PSRC1; BCAR1, CTRB1/BCAR1; GATAD2A, GATAD2A/TSSK6/NDUFA13/YJEFN3/CILP2; ABCB9, ABCB9/OGFOD2/PITPNM2.