Fig. 1.
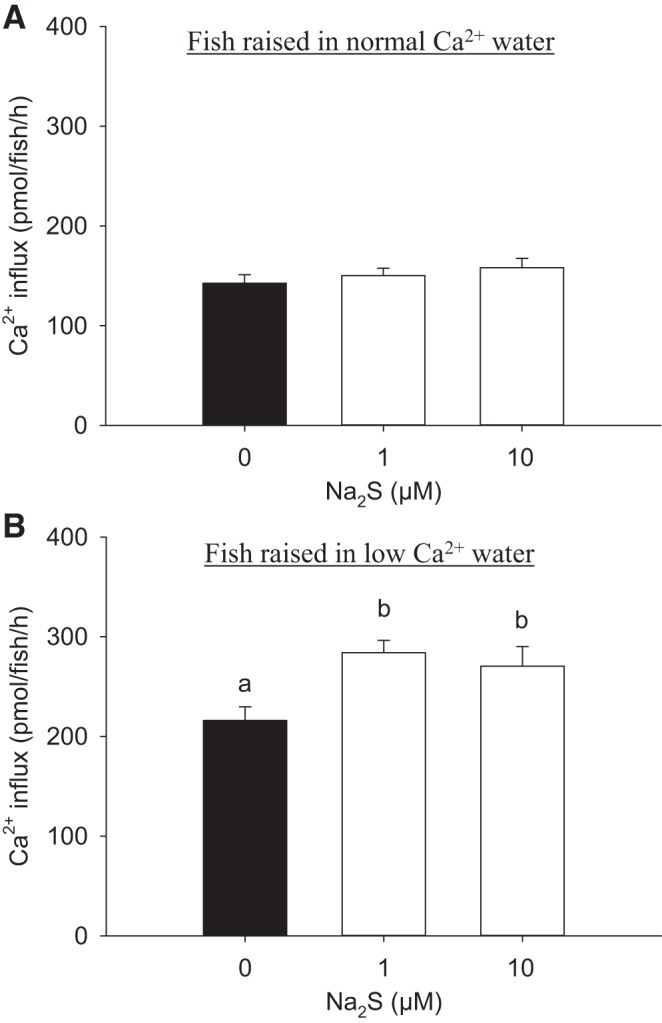
Acute exposure to sodium sulfide (Na2S) increases Ca2+ influx in fish acclimated to low-Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]) of water. The effects of Na2S exposure on Ca2+ influx in larval zebrafish [4 days postfertilization (dpf)] acclimated to normal [Ca2+] (250 μM; A) or low-[Ca2+] (25 μM; B) water for 3 days, beginning at 1 dpf, are shown. Influx of Ca2+ was measured in normal [Ca2+] water for both experiments. Values are means ± SE; N = 6. a,b Different letters represent a statistical difference from each other (one-way ANOVA, followed by a Holm-Sidak post hoc test; P < 0.05).
