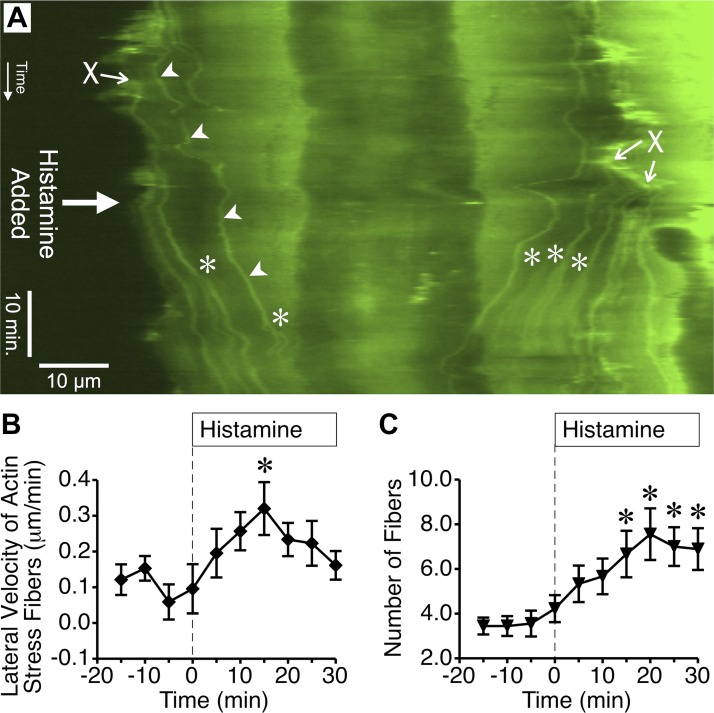
Fig. 2.
Histamine promotes lateral migration of cortical actin fiber bundles to the center of the cell. A: in this kymograph generated from time-lapse images of an endothelial cell expressing GFP-actin, the location where individual actin fibers cross the kymograph line over time can be observed. The beginning of the time-lapse series is at the top. Arrowheads denote where one individual actin fiber crosses the kymograph line (horizontal dimension) over time (vertical dimension). The fibers often form at the periphery of the cell (denoted by X) and travel toward the center. After 10 μM histamine was added, more fibers moved toward the center of the cell. Additional fibers also appeared due to the formation and movement of bifurcations. *Denotes where a stress fiber bifurcation crossed the kymograph line. B: mean lateral velocity of actin stress fibers over 5-min periods before and after treatment with 10 μM histamine was calculated using kymographs of nine different cells treated with histamine in three different experiments. C: mean number of actin fibers obtained from the same kymographs of histamine-treated cells for each 5-min period. In B and C, *P < 0.05 vs. baseline (0-min time point).