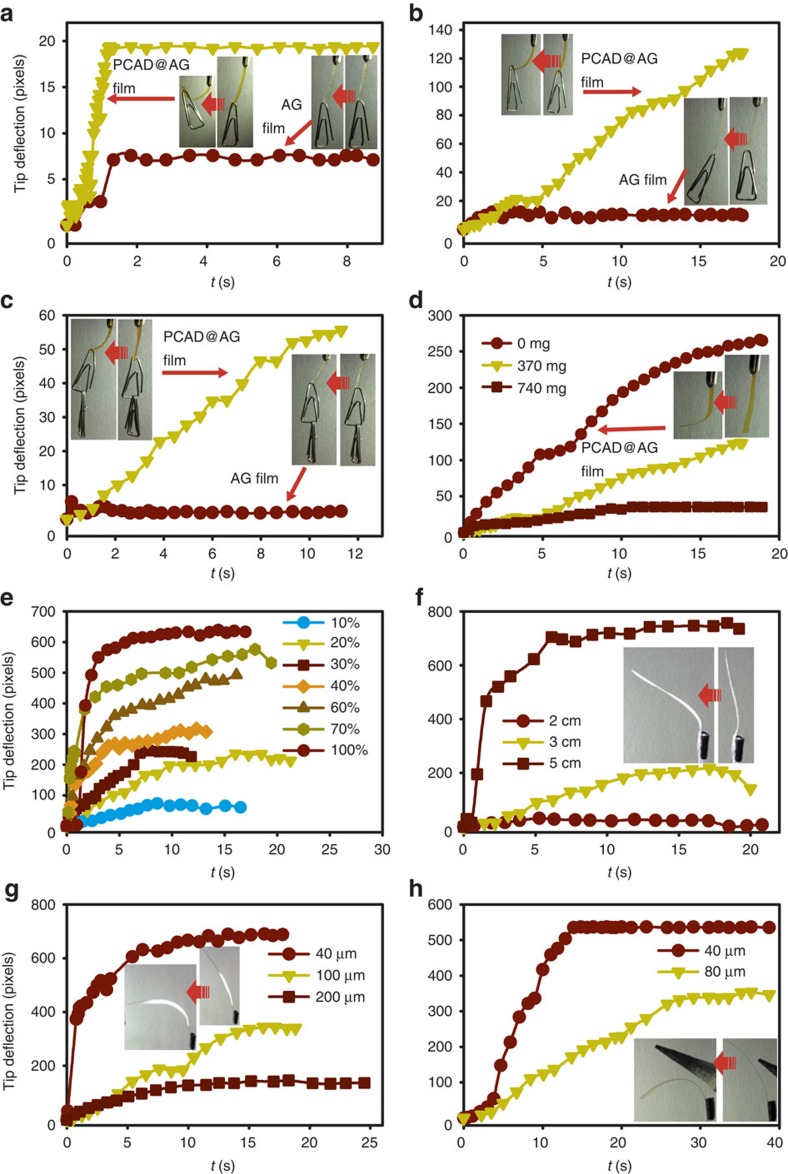
Figure 2. Performance of bending PCAD@AG films.
The y axis (in pixels) is the relative deflection of the tip of the film (for details on the kinematic analysis, see Supplementary Methods). The inset in each figure shows snapshots of the bending films. (a) Humidity-induced bending of films of PCAD@AG (16 mg) and pure AG (15 mg) of size 2 cm × 0.5 cm × 100 μm loaded with a cargo of 370 mg. (b) Humidity-induced bending of films of PCAD@AG and pure AG of size: 2 cm × 0.5 cm × 200 μm carrying a cargo of 370 mg (note the different scale on the y axis with a). (c) Performance of doped versus undoped film in humidity-induced bending (film size: 1 cm × 0.5 cm × 200 μm, cargo weight: 1,110 mg). (d) Effect of cargo weight on humidity-induced bending (film size: 2 cm × 0.5 cm × 200 μm, cargo weight: 370 mg and 1,110 mg). (e) Effect of ultraviolet power on photochemical bending (film size: 4 cm × 0.5 cm × 40 μm, ultraviolet power: 2–20 mW cm−2). (f) Effect of the length of the strip on the photochemical bending (ultraviolet light power: 20 mW cm−2). The numbers refer to the length of the strips. (g) Effect of film thickness on photochemical bending (ultraviolet power: 20 mW cm−2). (h) Effect of film thickness on the thermally induced bending of the films. The tip of a heated metal pin used as heat source is shown in the inset.