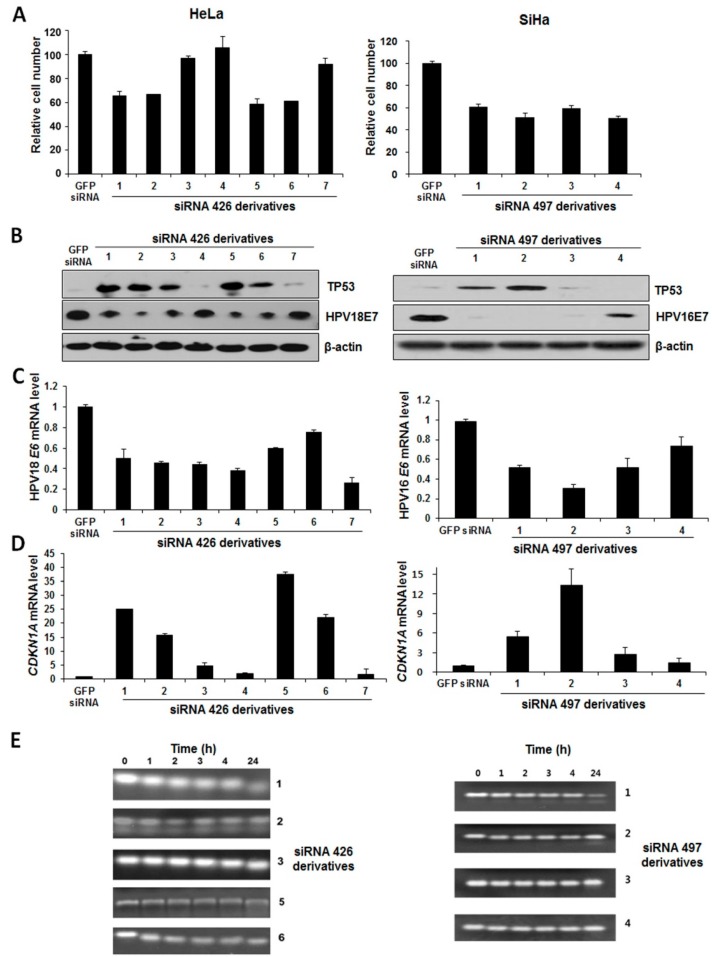
Figure 3.
Determining the stability and silencing activities of chemically-modified derivatives of HPV16- and 18 E6/E7-specific lead siRNAs. (A) Trypan blue assay showing the number of viable HeLa cells transfected with 2ʹ-OMe-modified derivatives of siRNA 426 and SiHa cells transfected with 2ʹ-OMe modified derivatives of siRNA 497. GFP-specific siRNA (control siRNA) served as controls; (B) Silencing efficiency of 2ʹ-OMe-modified siRNA derivatives on E7 expression and changes in TP53 expression were also analyzed by Western blotting. β-actin was used as a loading control; (C) E6 and (D) CDKN1A mRNA expression as determined by qRT-PCR; and (E) Gel electrophoresis analysis showing the serum stability of 2ʹ-OMe-modified siRNA derivatives. Unmodified (Lane 0) and modified siRNA 426 or 497 derivatives were analyzed by electrophoresis on 15% native polyacrylamide gels.