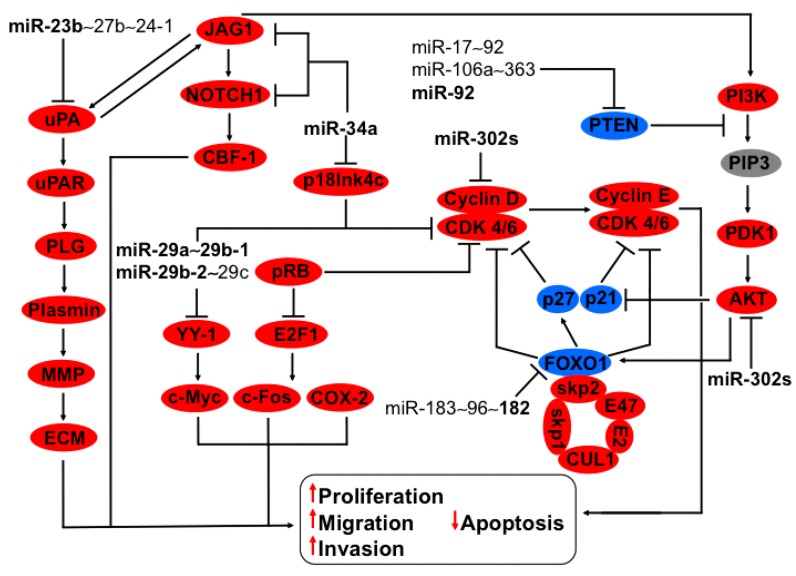
Figure 3.
Regulation of JAG1-NOTCH1-uPA, Cyclin D-CDK4/6-p21-p27, and PI3K-PDK1-AKT1 cell signaling by members of the miR-23b~27b~24-1, miR-29a~29b-1, miR-29b-2~29c, miR17~92, miR183~96~182, and miR-302s clusters. MiR-34a, a member of the miR-34 family, downregulates JAG1 and NOCTH1 expression. JAG1 is activated by uPA inducing ECM reorganization via plasminogen-plasmin-MMP, inducing the hallmarks of cancer. Protein expression of uPA is decreased by miR-23b, a member of the cluster 23b~27b~24-1. The complex cyclin D-CDK4/6 phosphorylates RB inducing the liberation of E2F, favoring c-Myc, c-Fos and COX-2 transcription provoking cellular division. Cellular division progression is regulated by the inhibition of cyclin D via the miR-302s cluster and CDK4/6 through p18Ink4c, p21, and p27. The PI3K-PDK1-AKT1 axis decreases p21 and p27 protein expression, delivering CDK4/6 to be complexed with cyclin D. This signaling pathway is regulated by the downregulation of AKT due to the miR-302s cluster increasing p21 and p27 proteins, thereby inhibiting the complex cyclin D-CDK4/6. CDK4/6 is inhibited by p18Ink4c, which in turn is downregulated by miR-34a, inducing apoptosis and causing proliferation to diminish. Another point of control is given by the miR-29a~29b-1 cluster hindering CDK4/6, which provokes inhibition of the complex cyclin D-CDK4/6. YY-1, a target of the cluster miR-29a~29b-1, induces transcription of c-Myc in the absence of this cluster common in cervical cancer. Cell cycle continuity is dependent on the levels and the complex formed of cyclin D-CDK4/6 and cyclin E-CDK4/6. FOXO1 could directly hinder CDK4/6, thus impeding the formation and activation of the complex cyclin D-CDK4/6 and cyclin E-CDK4/6 and indirectly via p27. Cyclin D is indirectly upregulated by miR-182, one member of the cluster miR183~96~182, through FOXO1 downregulation conducing to proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis induction. These cellular processes are enhanced via FOXO1 phosphorylation by PI3K-PDK1-AKT, which is recognized by skp2, a subunit of the skip1/cul1/F-box ubiquitin protein complex, targeting it to degradation via proteasomes. MiR-92 diminishes the expression of PTEN, triggering PI3K-PDK1-AKT signaling, which is conducive to FOXO1 reduction. In bold are the miRNAs with effect on genes with validated experimental data.