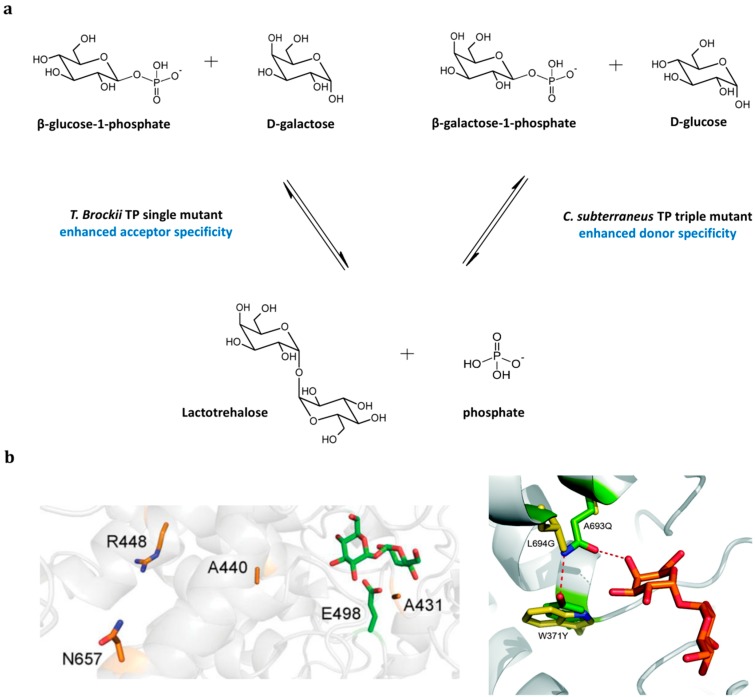
Figure 6.
Enhancing acceptor and donor specificity of T. brockii trehalose phosphorylases (TP) and C. subterraneus TP via random mutagenesis and rational design, respectively. (a) Reversible conversions of β-Glc-1P with d-galactose and β-Gal-1P with d-glucose into lactotrehalose, catalyzed by the T. brockii TP-single mutant (R448S) with enhanced acceptor specificity, and the C. subterraneus TP-triple mutant (L694G/A693Q/W371Y) with enhanced donor specificity, respectively; (b) Active sites of T. brockii TP (left) and C. subterraneus TP (right) with the positions subjected to mutagenesis indicated. For T. brockii TP, the mutated R448-residue is shown in orange/blue amongst other mutated residues from the same study, and the trehalose substrate with the catalytic residue (E498) in green. In the C. subterraneus TP active site, the three mutagenized positions (L694G/A693Q/W371Y) causing a switch in donor specificity are indicated in green with the corresponding wild-type residues shown in yellow. The lactotrehalose substrate is indicated in orange [66,67].