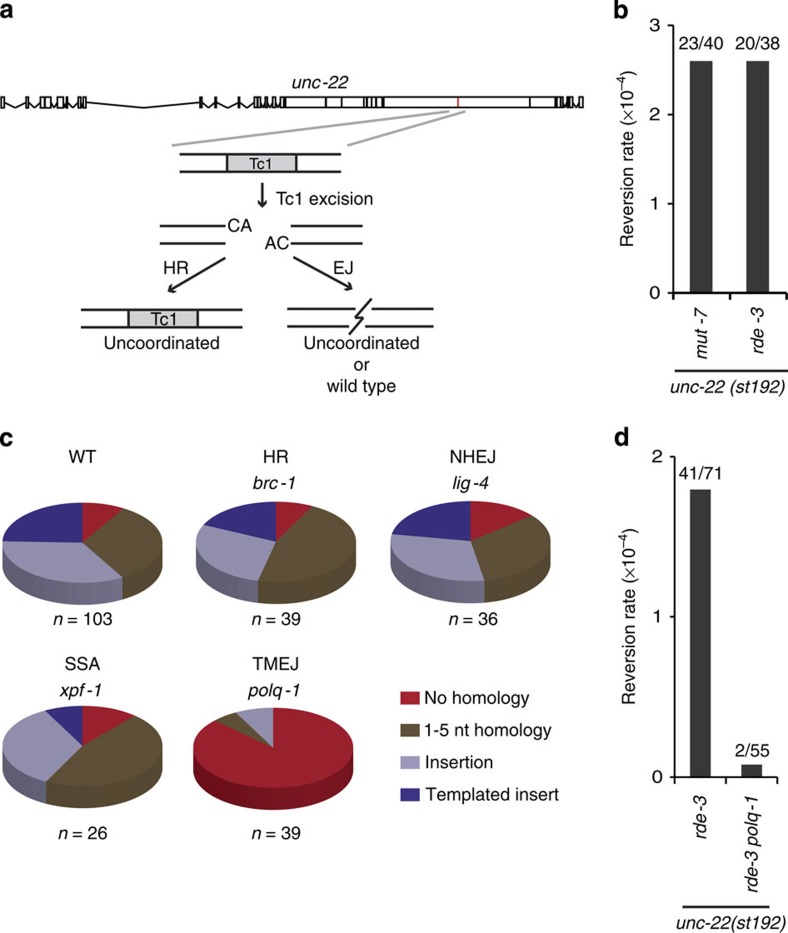
Figure 1. Error-prone repair of transposon-induced DSBs requires POLQ-1.
(a) Schematic representation of the experimental system to monitor repair of Tc1-induced DSBs. Tc1-encoded transposases can excise a frame-disrupting Tc1 element (unc-22::st192) from the endogenous unc-22 gene, thus resulting in a DSB within the unc-22 ORF with non-complementary 3′ overhangs of two nucleotides. In case of repair through HR, the original (Tc1-containing) sequence will be restored without affecting the phenotype of progeny cells. Error-prone EJ can lead to unc-22 ORF correction, which, when occurring in germ cells, will result in wild-type-moving progeny born out of uncoordinatedly moving unc-22 mutant animals. (b) Reversion frequencies of Tc1 for two different genetic backgrounds (rde-3 and mut-7) that de-repress transposon silencing53. For each mutant background, ∼20 populations were scored for the presence of revertants and experiments were performed in duplicate. The total number of populations that were assayed and the number of populations that contained at least one revertant animal are indicated. Populations contained, on average, 2,000 animals. (c) Distribution of footprints in unc-22(st192) for the indicated genomic backgrounds; all strains were also rde-3 deficient. The number of independently derived reversion alleles is depicted underneath. Distinct footprints (26 in repair-proficient animals) were classified into the following four separate categories: (i) simple deletions without homology at the deletion junction (red), (ii) simple deletions with 1–5 bp of sequence homology at the deletion junction (brown), (iii) deletions that also contained insertions (light blue), and (iv) deletions with associated insertions that were identical to sequences immediate flanking the break (blue). (d) Quantification of the unc-22(st192) reversion frequency in rde-3 and polq-1; rde-3 mutant backgrounds. The number of populations that were assayed and the number of populations that contained at least one revertant animal are indicated. Populations contained, on average, 2,400 animals.